Nobel Physics Prize Honors Pioneers of Machine Learning with Neural Networks
John Hopfield and Geoffrey Hinton awarded Nobel Prize in Physics for groundbreaking work in machine learning. Their discoveries enable AI systems to process data similarly to the human brain.
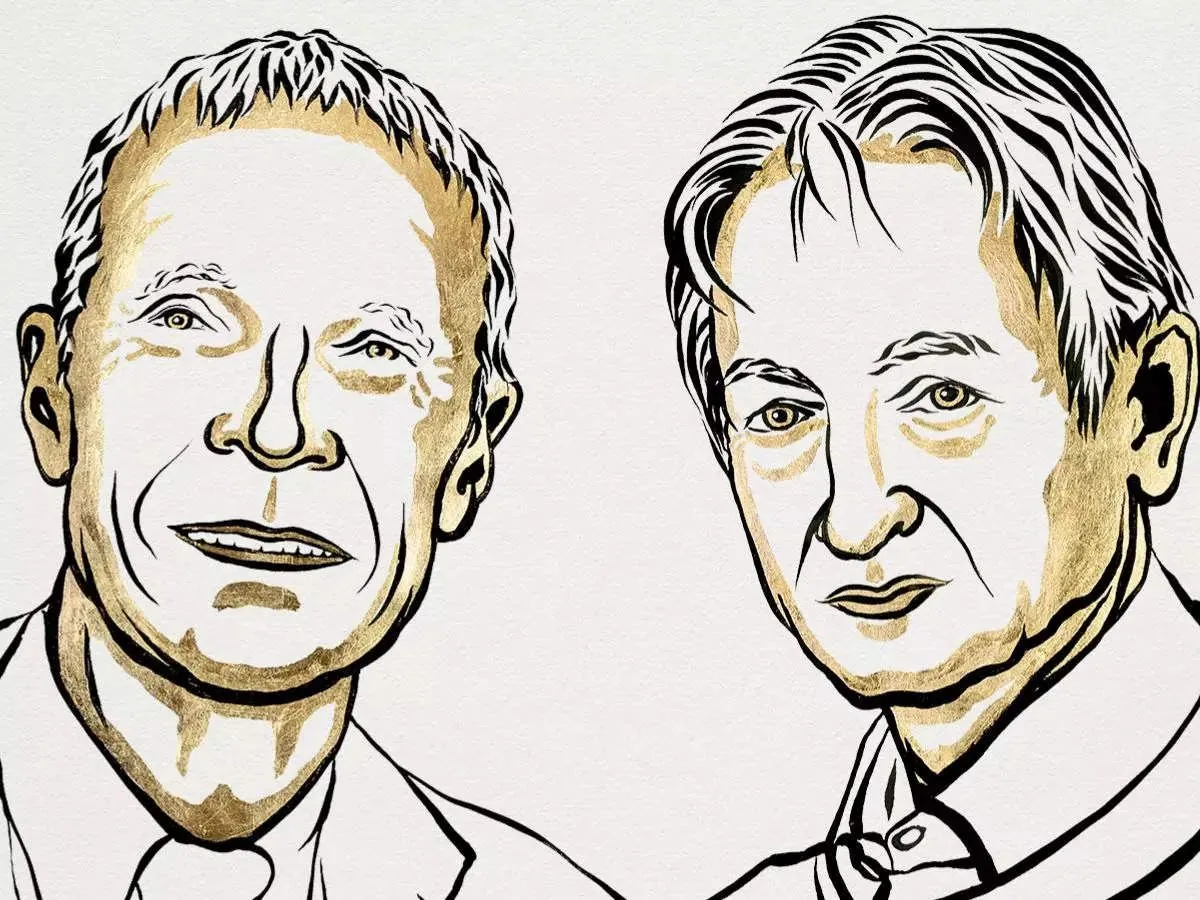

The 2024 Nobel Prize in Physics has been awarded to John Hopfield of Princeton University and Geoffrey Hinton of the University of Toronto for their groundbreaking contributions to machine learning with artificial neural networks. This prestigious recognition, first awarded in 1901, highlights the growing importance of artificial intelligence (AI) in modern science and technology.
The Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences acknowledged the laureates' "foundational discoveries and inventions that enable machine learning with artificial neural networks." Machine learning, a term coined by Arthur Samuel in 1959, refers to the development of computer systems that can learn and adapt without explicit programming. The work of Hopfield and Hinton has paved the way for systems that process data in a manner similar to the human brain.
Hinton, often referred to as the "Godfather of AI," expressed both excitement and concern about the future of AI. In a phone interview with the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences, he stated:
"We have no experience with what it's like to have things smarter than us. It's going to be wonderful in many respects.... It'll mean huge improvements in productivity. But we also have to worry about a number of possible bad consequences, particularly the threat of these things getting out of control."
Hinton's cautionary stance is particularly noteworthy, given that he left his position at Google in 2023 due to concerns about AI advancements. His work on backpropagation in the 1980s was crucial for the development of deep learning, a subset of machine learning that gained prominence in the 2010s.
The impact of machine learning extends far beyond the realm of computer science. Applications of this technology can be found in diverse fields such as astrophysics, medical diagnostics, and climate modeling. For instance, AI has been used to discover new antibiotics, predict protein structures, and improve climate models and weather predictions.
John Hopfield's contributions, particularly his work on associative neural networks, have been equally influential. The Hopfield networks, introduced in 1982, are a form of recurrent artificial neural network that have found applications in various domains.
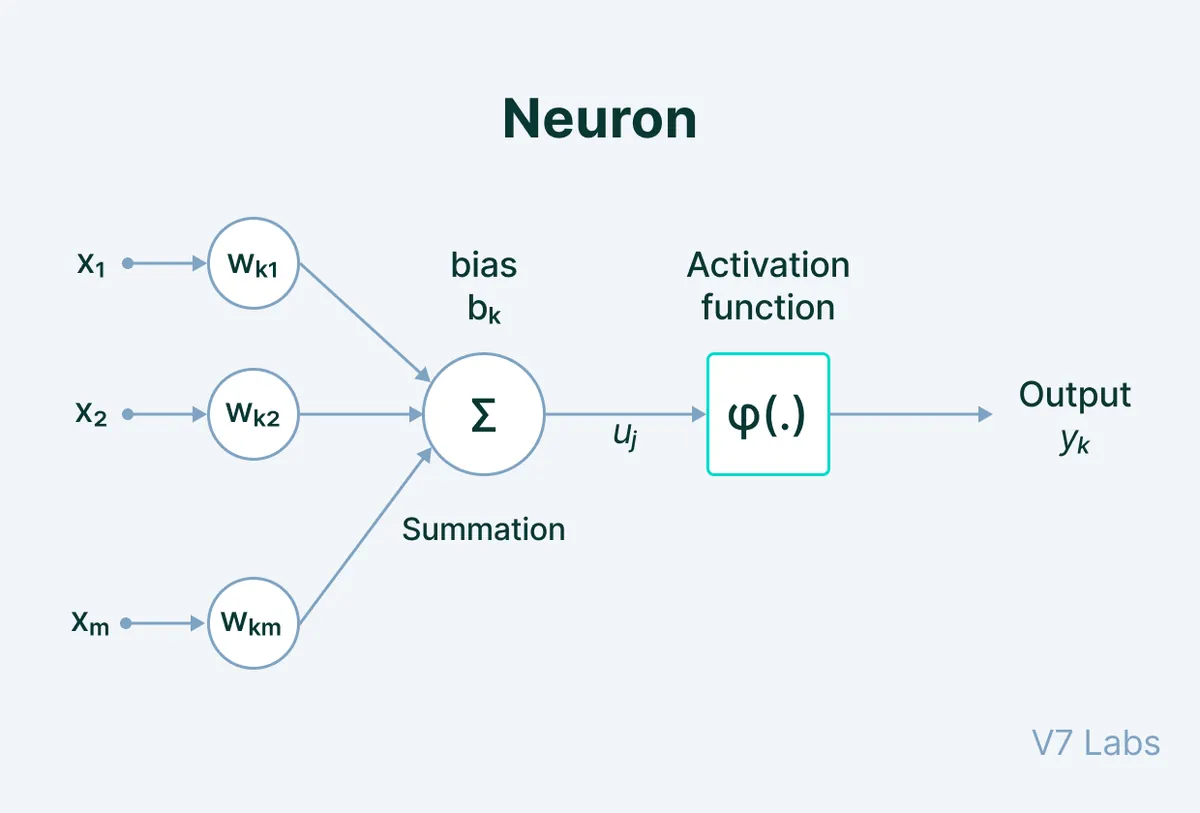
The history of artificial neural networks dates back to the 1940s, with significant milestones along the way. The first artificial neural network computer, SNARC, was built in 1951, while the perceptron, an early neural network model, was invented in 1957 by Frank Rosenblatt. The field of AI itself was formally introduced at a conference in 1956, with the first AI program, the Logic Theorist, created a year earlier.
As AI continues to advance, it has achieved remarkable feats, such as defeating human champions in chess, Go, and poker. Neural networks have even been used to generate art and music, pushing the boundaries of creativity and computation.
However, the rapid progress in AI has also raised significant ethical and safety concerns. The concept of AI ethics has become a major focus in recent years, with researchers and policymakers grappling with issues such as bias in AI systems, privacy concerns, and the potential for job displacement.
The Nobel Prize in Physics serves as a reminder of the transformative potential of AI and machine learning. As we look to the future, the work of Hopfield and Hinton will continue to shape our understanding of artificial intelligence and its impact on society.