California Battles Multiple Wildfires Amid Intense Fire Season Start
Southern California faces multiple wildfires, forcing evacuations and threatening thousands of homes. Cooler temperatures bring hope for firefighters as the state experiences an unusually active start to its fire season.
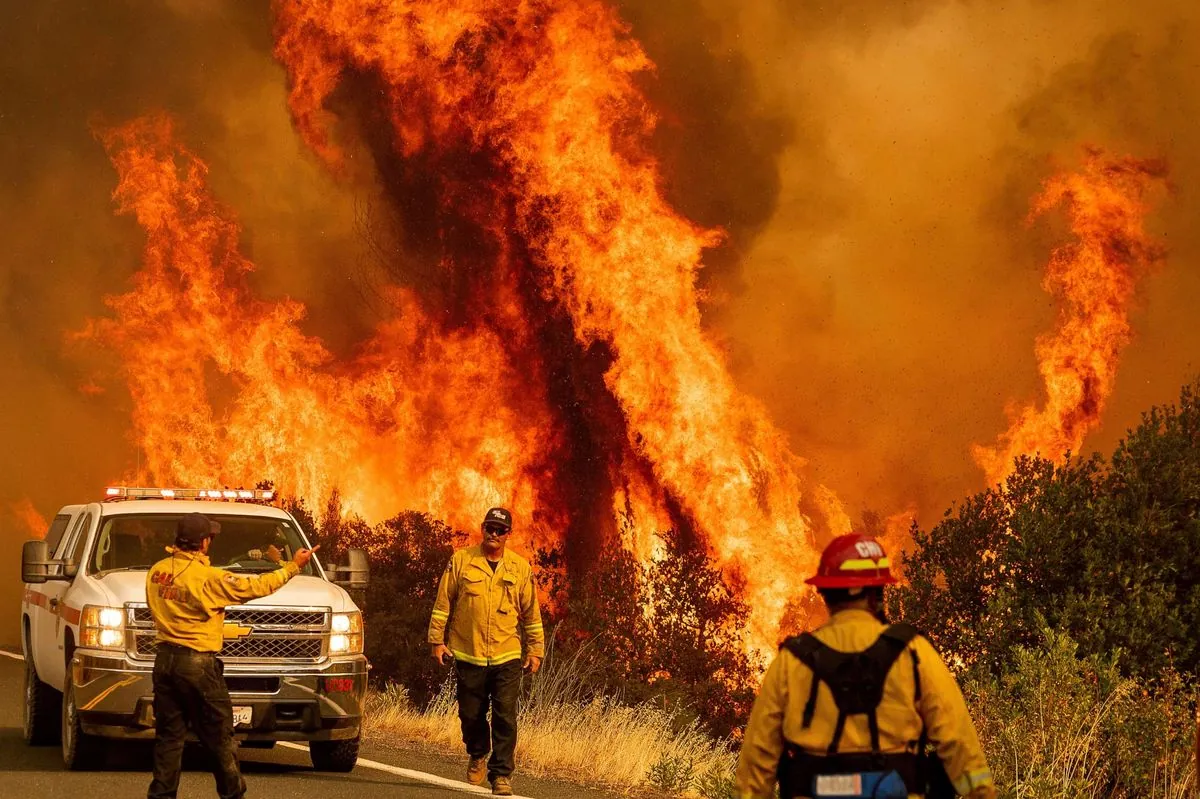

Southern California is currently grappling with multiple wildfires, forcing thousands to evacuate and endangering numerous homes and structures. The situation highlights the state's increasingly challenging fire seasons, exacerbated by climate change and prolonged dry periods.
The Bridge Fire near Wrightwood, a community in the San Gabriel Mountains, has prompted evacuations. Alex Luna, a 20-year-old missionary, described the scene as the sky transitioned from red to black within 90 minutes. Luna noted, "Ash was falling from the sky like if it was snowing." This vivid description underscores the intensity of the fire and its impact on local residents.
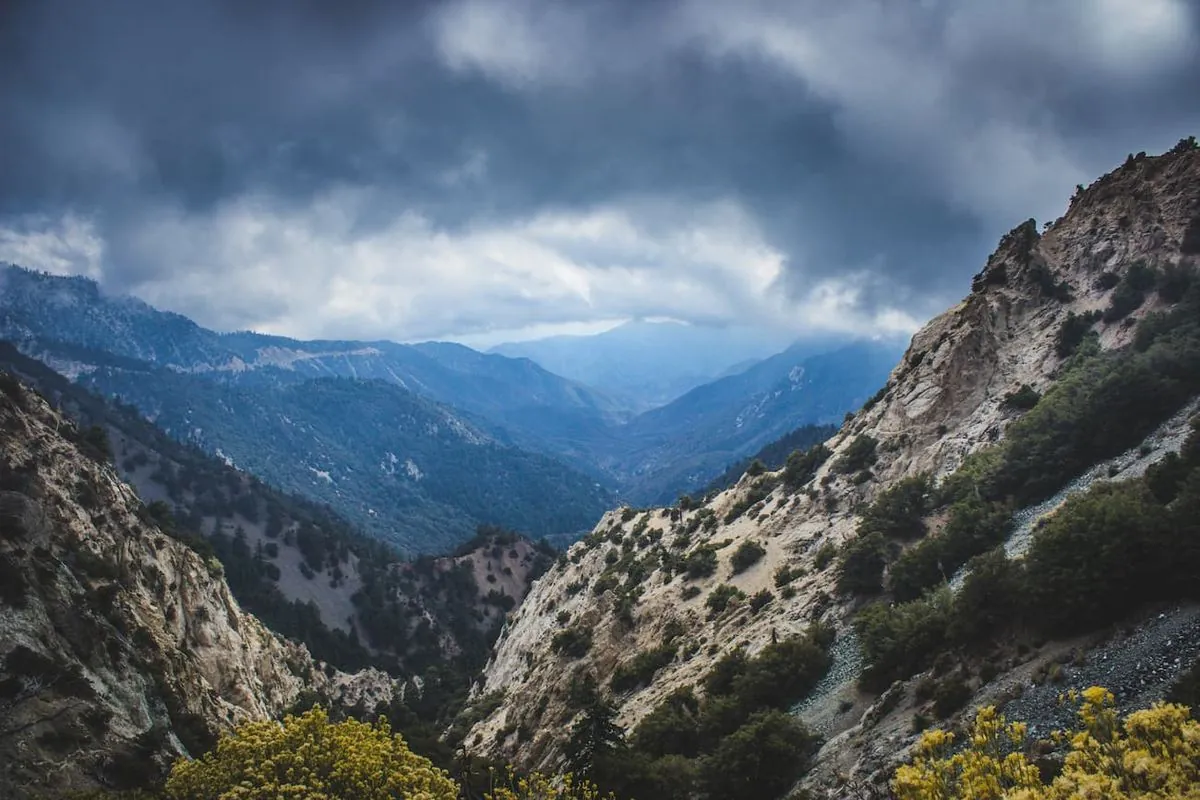

The San Gabriel Mountains, where Wrightwood is located, are part of the Transverse Ranges in Southern California. These mountains were formed by tectonic activity along the San Andreas Fault, contributing to the region's unique geography and fire-prone conditions.
Simultaneously, the Line Fire is threatening the popular ski town of Big Bear and surrounding areas. Authorities have expanded evacuation orders, with approximately 65,600 homes and buildings at risk. The fire has already consumed over 51 square miles (132 square kilometers) of vegetation.
Big Bear Lake, a reservoir in the San Bernardino Mountains, was created by a dam built in 1884. The area's popularity among outdoor enthusiasts adds to the complexity of managing evacuations and protecting property.
In Orange County, the Airport Fire is rapidly spreading, having burned more than 30 square miles (78 square kilometers) with no containment as of the report. This fire, ignited by a spark from heavy equipment used by public workers, has damaged communication towers and poses a threat to nearby communities.
"The fire was burning away from homes in Orange County, but there are 36 recreational cabins in the area."
The use of aircraft in firefighting, which began in California in the 1930s, has become crucial in combating these wildfires. Helicopters and planes are being utilized alongside bulldozers and ground crews to control the spread of flames.
California's fire ecology plays a significant role in many of the state's ecosystems, with some plant species adapted to regular fires. However, the increasing frequency and intensity of wildfires due to climate change are pushing these adaptations to their limits.
As of September 11, 2024, California has already experienced nearly three times as much acreage burned compared to the entire previous year. This alarming statistic reflects the state's extended fire season, which now poses year-round risks in some areas.
The economic impact of these wildfires is substantial, with recent years seeing annual costs estimated in the tens of billions of dollars. This includes not only direct damage but also long-term effects on air quality, tourism, and public health.
While cooler temperatures have recently brought hope for firefighters to make progress, the situation remains critical. The ongoing battle against these wildfires serves as a stark reminder of the challenges faced by California and other western states in managing and mitigating the impacts of increasingly severe fire seasons.