Innovative Strategies Tackle Post-Pandemic Chronic Absenteeism in US Schools
Schools across the US are implementing creative solutions to combat persistent chronic absenteeism, a lingering effect of the COVID-19 pandemic. From lunchtime sports to mentorship programs, educators are striving to re-engage students.
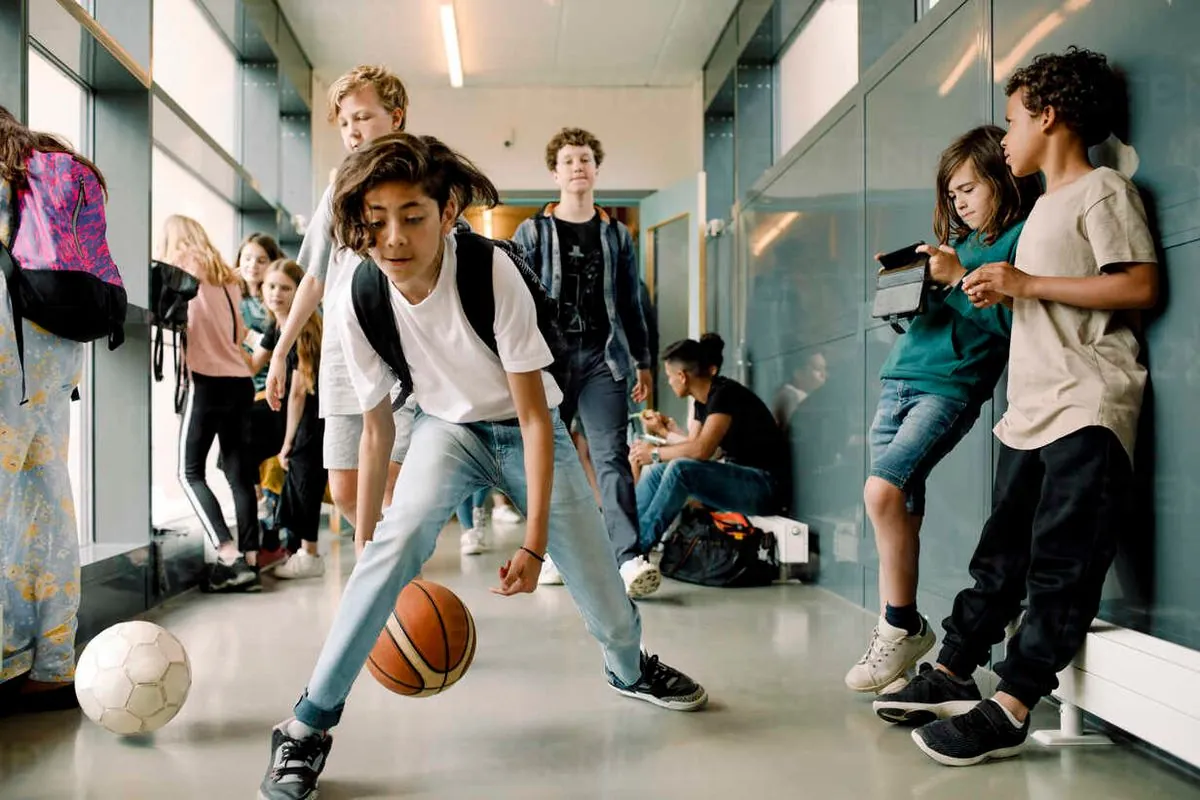
In the aftermath of the COVID-19 pandemic, Flerentin "Flex" Jean-Baptiste's story exemplifies the ongoing struggle with chronic absenteeism in American schools. The 16-year-old student at Medford High School outside Boston initially missed 30 days of his freshman year, leading to grade repetition. However, an innovative approach by his principal dramatically improved his attendance.
"It gave me something to look forward to."
This simple yet effective strategy of offering organized sports during lunch for students who attend all classes has contributed to a significant reduction in chronic absenteeism at Medford High. The school's chronic absence rate dropped from 35% in March 2023 to 23% in March 2024, marking one of the steepest declines among Massachusetts high schools.
The issue of chronic absenteeism, defined as missing 10% or more of school days in a year, remains a nationwide concern. According to data collected by The Associated Press and Stanford University economist Thomas Dee, approximately 25% of students in the 2022-23 school year were chronically absent across 42 states and Washington, D.C. This represents about 12 million children, a substantial increase from the pre-pandemic rate of 15%.

Schools are implementing various strategies to address this challenge. In Oakland, California, where chronic absenteeism rose from 29% pre-pandemic to 53% in 2022-23, a grant-funded program was launched in spring 2023. The initiative paid 45 students $50 weekly for perfect attendance and provided them with mentors. Zaia Vera, the district's head of social-emotional learning, reported that over 60% of participants improved their attendance.
The connection between mental health and absenteeism has become increasingly apparent. Research shared by University of Southern California professor Morgan Polikoff found that almost a quarter of chronically absent kids had high levels of emotional or behavioral problems, compared to just 7% of kids with good attendance.
In response to these challenges, more than a dozen states now allow students to take mental health days as excused absences. However, experts like Hedy Chang of Attendance Works caution that staying home can become a vicious cycle, leading to further disengagement and academic struggles.
Practical solutions are also proving effective. In Fresno, California, Fort Miller Middle School addressed two primary reasons for absenteeism by providing a washer and dryer for families' use and a Chevy Suburban to pick up students who missed the bus. These measures contributed to reducing the district's chronic absenteeism rate from 50% to 35% in 2022-23.
As schools continue to grapple with the lingering effects of pandemic-era disruptions, innovative approaches and a renewed focus on student engagement are crucial. The ongoing efforts to improve attendance reflect the understanding that regular school attendance is fundamental to academic success and overall student well-being.