Kroger-Albertsons Merger Faces Federal Scrutiny: What's at Stake?
Kroger and Albertsons' proposed $24.6 billion merger faces legal challenges from the FTC and several states. The outcome could significantly impact grocery prices, store availability, and working conditions for millions of Americans.
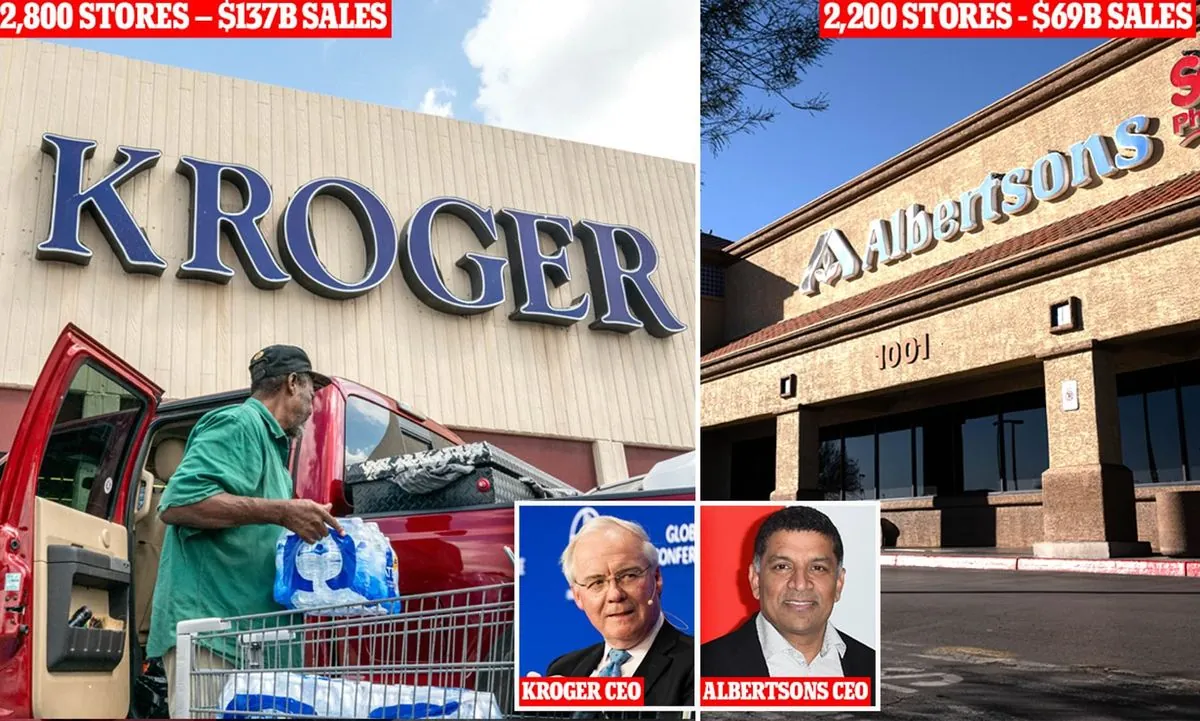

Kroger and Albertsons, two of America's largest supermarket chains, are preparing to defend their proposed $24.6 billion merger against federal regulators. This potential union, which would create the largest supermarket merger in U.S. history, has sparked significant debate and legal challenges.
The companies argue that the merger would enhance their ability to compete with various retail formats, including supercenters, discount stores, and online platforms. However, the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) and several states have taken legal action to prevent the deal, citing concerns about reduced competition, increased grocery prices, and potential negative impacts on employee working conditions.
Legal proceedings commenced on August 26, 2024, in the U.S. District Court in Portland, Oregon. The FTC is seeking a temporary injunction to halt the merger while an administrative court reviews the case. Concurrently, separate lawsuits initiated by Colorado and Washington are scheduled to begin in September 2024.
This proposed merger raises several critical questions for consumers and the grocery industry:
Merger Motivations: Kroger and Albertsons claim the deal would improve their competitive position. Founded in 1883 and 1939 respectively, these companies have a long history in the U.S. grocery market. The combined entity would generate annual revenues of approximately $200 billion, potentially rivaling Walmart, which currently holds about 26% of the U.S. grocery market share.
Price Impacts: Critics argue that reduced competition could lead to higher grocery prices. The FTC, established in 1914 to prevent anticompetitive practices, is particularly concerned about this aspect. The Clayton Antitrust Act of 1914 and the Robinson-Patman Act of 1936 provide legal frameworks to address such concerns.
Store Closures: The merger could result in store divestitures to address antitrust concerns. Kroger operates over 2,700 stores across 35 states, while Albertsons has more than 2,200 locations in 34 states and Washington D.C. Any closures could affect local communities and consumer access to groceries.
Worker Effects: Labor advocates worry about potential negative impacts on employee working conditions and job security.
Market Dynamics: The U.S. grocery market, valued at over $800 billion annually, has seen significant changes in recent years. Online grocery sales have grown to account for about 10% of total sales in 2023, a trend accelerated by the COVID-19 pandemic.

The outcome of this legal battle will have far-reaching implications for the U.S. grocery landscape. As the proceedings unfold over the next two weeks, consumers, industry observers, and government officials will be closely monitoring the situation to understand how this potential merger could reshape the future of grocery shopping in America.
"Our thorough investigation shows that this merger will result in higher prices for groceries and other essential household products, as well as worse experiences for shoppers and workers throughout the country."
The Hart-Scott-Rodino Antitrust Improvements Act requires companies to notify the FTC and Department of Justice of large mergers and acquisitions, highlighting the significance of this case in the broader context of U.S. antitrust law and consumer protection.