Ancient Roman Tombs with Vibrant Paintings Unveiled in Ashkelon, Israel
Two 1,700-year-old Roman tombs featuring well-preserved wall paintings will open to the public in Ashkelon, Israel. The site, discovered in the 1930s, has undergone extensive conservation efforts.
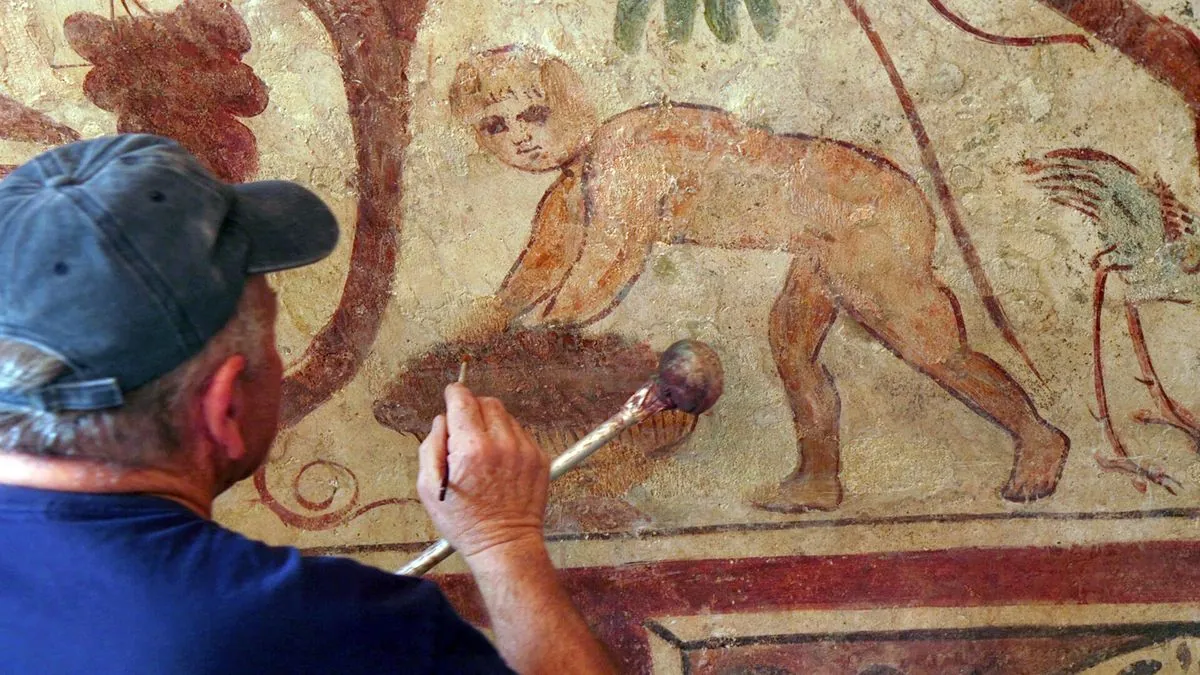

In a significant archaeological development, two Roman-era tombs dating back approximately 1,700 years have been prepared for public viewing in Ashkelon, Israel. These tombs, featuring remarkably well-preserved wall paintings, were initially unearthed by British archaeologists in the 1930s but remained closed to the public for nearly a century to protect their delicate artworks.
The Israel Antiquities Authority has announced that after extensive conservation efforts, these tombs will be accessible to visitors for the first time during the upcoming Sukkot holiday in October 2024. The site's opening marks a crucial milestone in preserving and sharing Ashkelon's rich historical heritage.
Anat Rasiuk, an archaeologist with the Antiquities Authority, expressed amazement at the paintings' excellent condition, considering their age and exposure to coastal environmental factors. The tombs, situated a few hundred meters from the beach, are believed to have been the final resting places for Roman aristocrats when Ashkelon was under Roman rule.
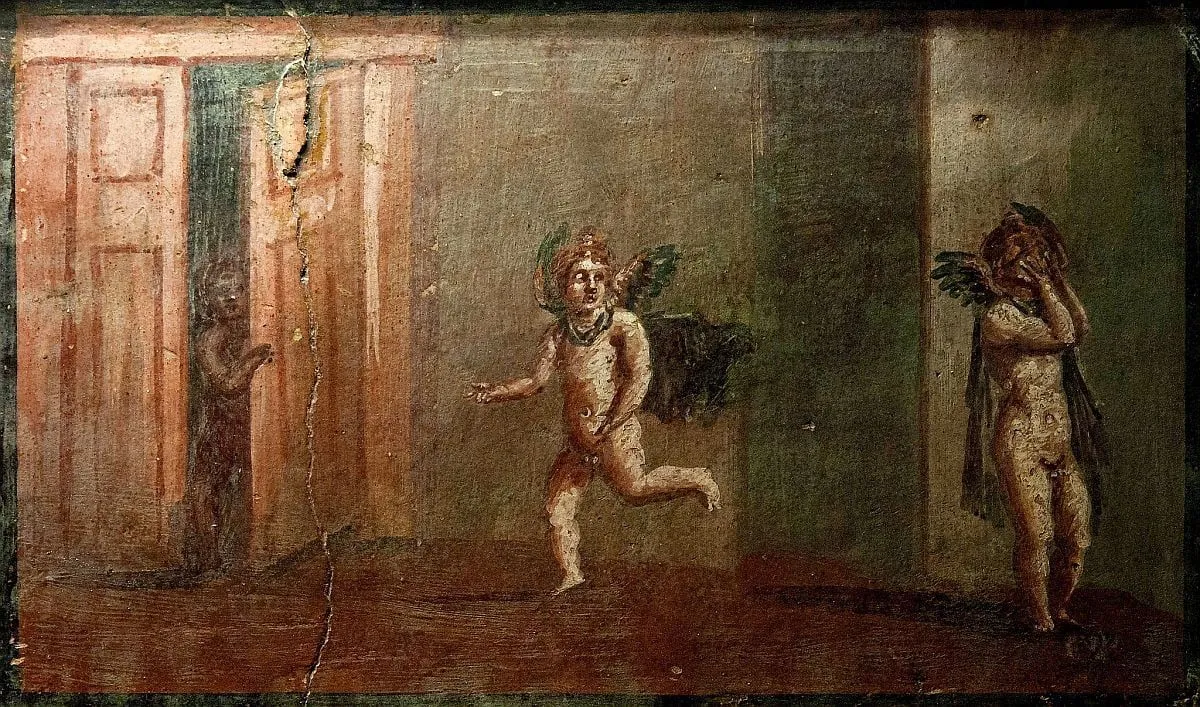
The wall paintings showcase a vibrant array of imagery, including:
- Grape vines intertwining with birds and animals
- Mythological figures from Greek and Roman traditions
- Nymphs adorned with lotus plant wreaths
- Children harvesting grapes
- A figure playing Pan's flute
- Representations of Demeter, the goddess of earth and grain
- The head of Medusa, with her characteristic snake-hair

The conservation process involved meticulous work, including removing some plaster paintings for off-site restoration and enhancing others with pigments matching the ancient paint. A second tomb from the 2nd century CE, also featuring colorful wall paintings, has been relocated to the new archaeological park.
Ashkelon's archaeological significance extends far beyond the Roman period. The city has been continuously inhabited for over 6,000 years and was once a major Canaanite seaport. It was also one of the five chief cities of the Philistines, mentioned in the Bible. Recent DNA studies have provided intriguing clues about the Philistines' potential European origins, dating back more than 4,000 years.
Throughout its long history, Ashkelon has seen numerous conquests and cultural influences. It was an important Byzantine center, later conquered by the Fatimid Caliphate, Crusaders, and Saladin. The city was even the birthplace of Herod the Great around 73 BCE. Modern Ashkelon was established as a development town in 1949 and has since become known for its archaeological treasures, including the "Ashkelon hoard" of silver coins from the 3rd-4th centuries CE.
While celebrating its ancient heritage, Ashkelon has also faced contemporary challenges. The city has been a target of rocket attacks from Gaza since 2001, and in May 2024, it experienced an incident where vessels involved in building a U.S. pier in Gaza beached on its coast during adverse weather conditions.
The opening of these Roman tombs to the public represents a significant step in showcasing Ashkelon's diverse historical layers, from ancient civilizations to modern times, offering visitors a unique glimpse into the region's rich past.