India's Economic Growth Slows in Q2 2024 Amid Election-Related Spending Cuts
India's GDP growth expected to moderate to 6.9% in April-June 2024, down from 7.8% in the previous quarter, due to reduced government spending during national elections. Despite slowdown, India likely to remain world's fastest-growing major economy.
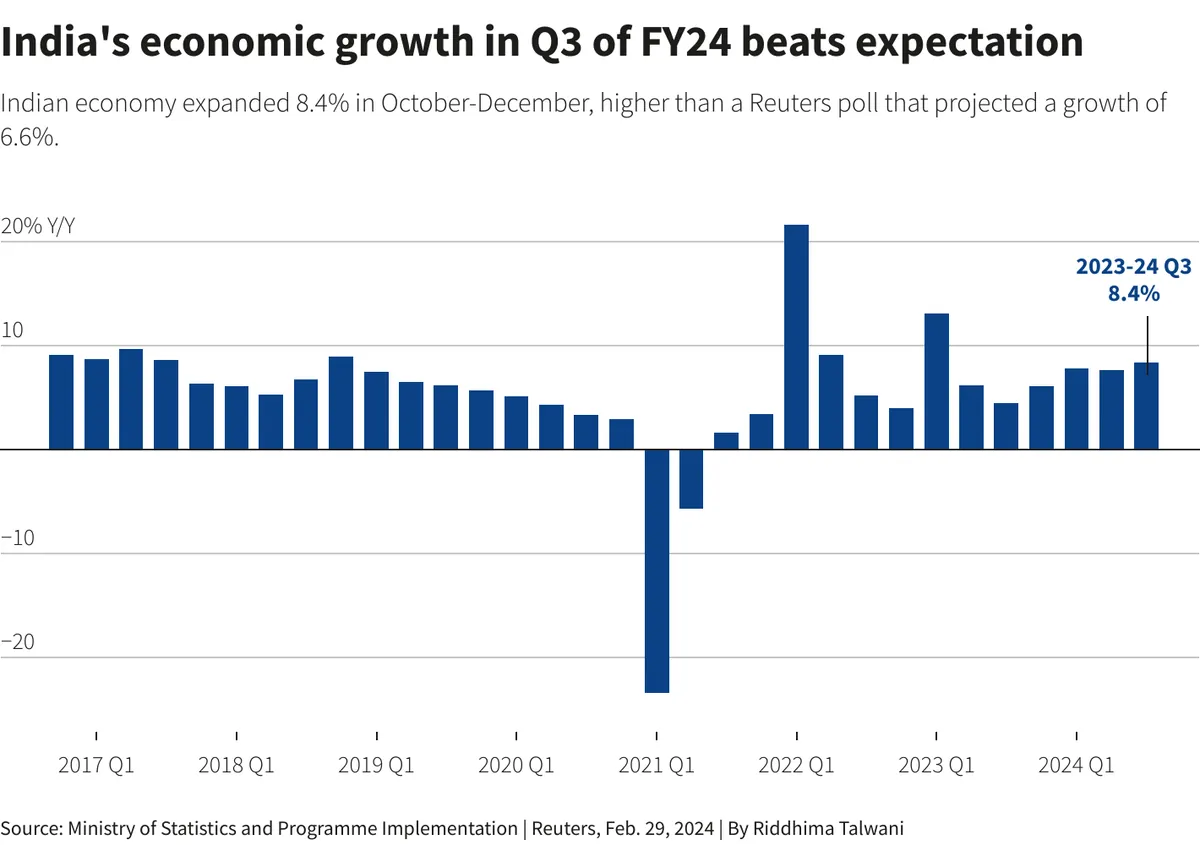
India's economic growth is projected to have decelerated in the April-June quarter of 2024, marking its slowest pace in a year. This moderation is primarily attributed to reduced government expenditure during the national election period that concluded in June.
According to a Reuters poll of 52 economists, India's gross domestic product (GDP) is estimated to have expanded by 6.9% annually in the second quarter of 2024, a notable decrease from the 7.8% growth recorded in the preceding quarter. Despite this slowdown, India is expected to maintain its position as the world's fastest-growing major economy.
The anticipated deceleration in growth can be largely attributed to the government's decision to curtail public spending ahead of the parliamentary elections. While Prime Minister Narendra Modi's Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP) secured another term in office, it did not retain its outright majority in the lower house.

Dhiraj Nim, an economist at ANZ, commented on the situation:
"The public spending slowdown was significant both by the centre and the states, especially on the capex front. So, there is the transitory element of growth slowdown. However...private consumption growth was better than the previous quarter and overall manufacturing and non-public services were steady."
It's worth noting that India's economy became the fifth largest globally by nominal GDP in 2022, showcasing its growing importance in the world economic landscape. The country's mixed economy system, combining elements of capitalism and socialism, has been undergoing reforms since 1991, moving towards a more open market structure.
Looking ahead, economists project India's growth to average 7.0% for the current fiscal year (2024-2025) and 6.7% for the next. These forecasts remain unchanged from previous estimates. The government has implemented measures to stimulate consumption, allocating substantial funds for rural spending and job creation in its first post-election budget.
India's large and growing middle class, estimated to exceed 350 million people, represents a significant driver of economic activity. However, challenges persist in translating overall growth into broad-based consumption. In the previous quarter, while GDP growth approached 8%, consumption - which accounts for over 50% of GDP - grew at only half that rate.
Kunal Kundu, India economist at Societe Generale, offered insights on the consumption outlook:
"We anticipate a modest improvement in domestic demand, although it has not yet emerged as a significant driver of growth...the sustained weakness in core inflation suggests that real consumption recovery is still a few quarters away."
Inflation remains a key factor influencing economic dynamics. As of July 2024, consumer price inflation stood at 3.54%, with expectations of averaging around 4.5% for the current and next fiscal years. The Reserve Bank of India (RBI), the country's central bank, closely monitors these trends to shape monetary policy.
India's economic landscape continues to evolve, with its IT sector serving as a major contributor to the economy and global exports. The country's demographic dividend, characterized by a large young population, is viewed as a potential economic advantage that could drive future growth and innovation.


































