India's Forex Reserves Drop $4.8 Billion, Rupee Hits Record Low
India's foreign exchange reserves fell to $670.12 billion, marking the largest decline in four months. The rupee reached a record low amid market volatility, prompting central bank intervention.
In a significant financial development, India's foreign exchange reserves experienced a substantial decline, reaching $670.12 billion as of August 9, 2024. This marks a $4.8 billion decrease from the previous week, representing the most substantial drop in four months.
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI), established on April 1, 1935, plays a crucial role in managing these reserves. The central bank intervenes in the foreign exchange market to mitigate excessive volatility in the rupee's value. This intervention, along with fluctuations in the value of foreign assets held in reserves, contributes to changes in foreign currency assets.
India's forex reserves, which surpassed Russia's in 2020, are composed of various elements:
- Foreign currency assets: $587,960 million
- Gold reserves: $59,239 million
- Special Drawing Rights (SDRs): $18,282 million
- Reserve Tranche Position: $4,638 million
It's worth noting that India's gold reserves rank as the 9th largest globally, highlighting the country's significant position in the international financial landscape.
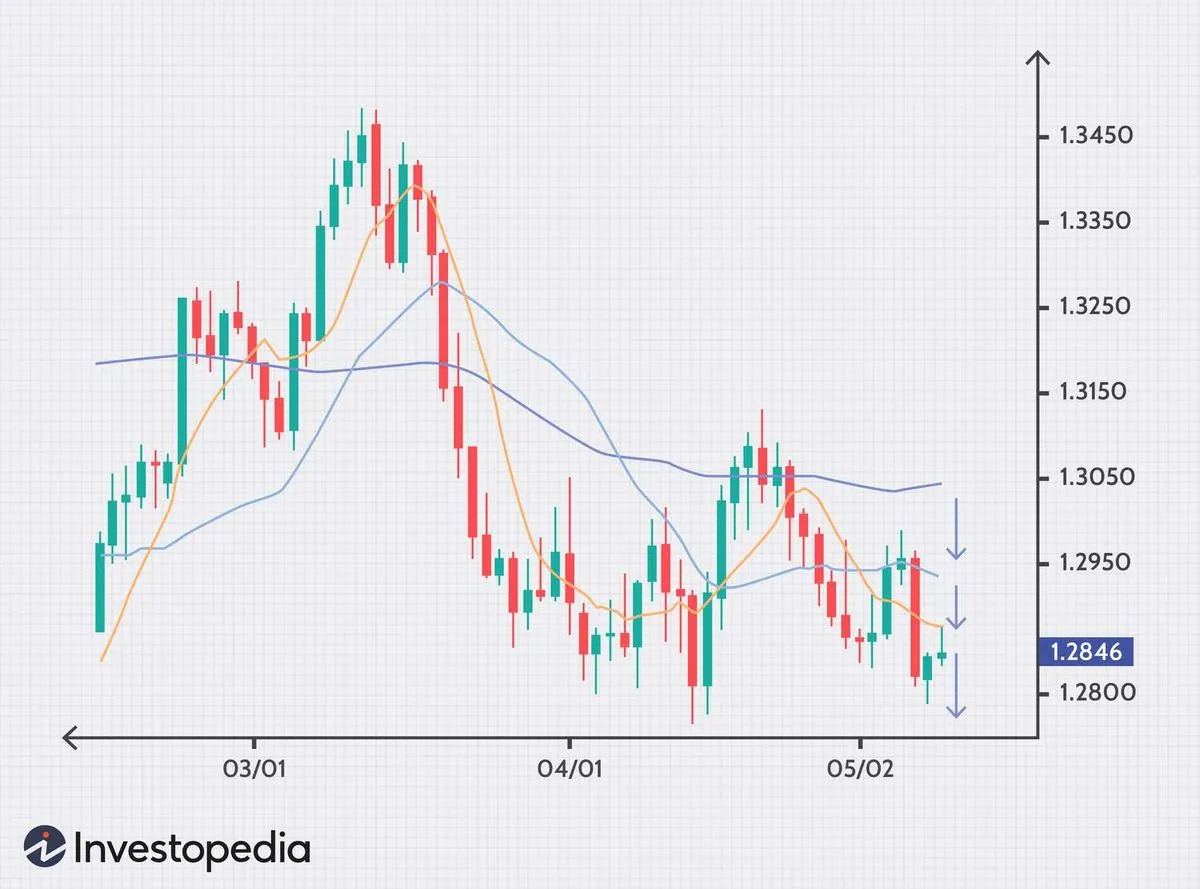
During the reporting week, the Indian rupee faced considerable pressure, reaching a record low of 83.9725 against the US dollar. This depreciation resulted in the worst weekly performance for the currency in over two months. By August 16, 2024, the rupee had stabilized at 83.94, remaining flat week-over-week.
The recent fluctuations in forex reserves and currency value occur against the backdrop of India's position as the world's fifth-largest economy by nominal GDP. The country's economic journey has been marked by significant milestones, including the introduction of the rupee as the official currency in 1947 and its transition to full convertibility on the current account in 1994.
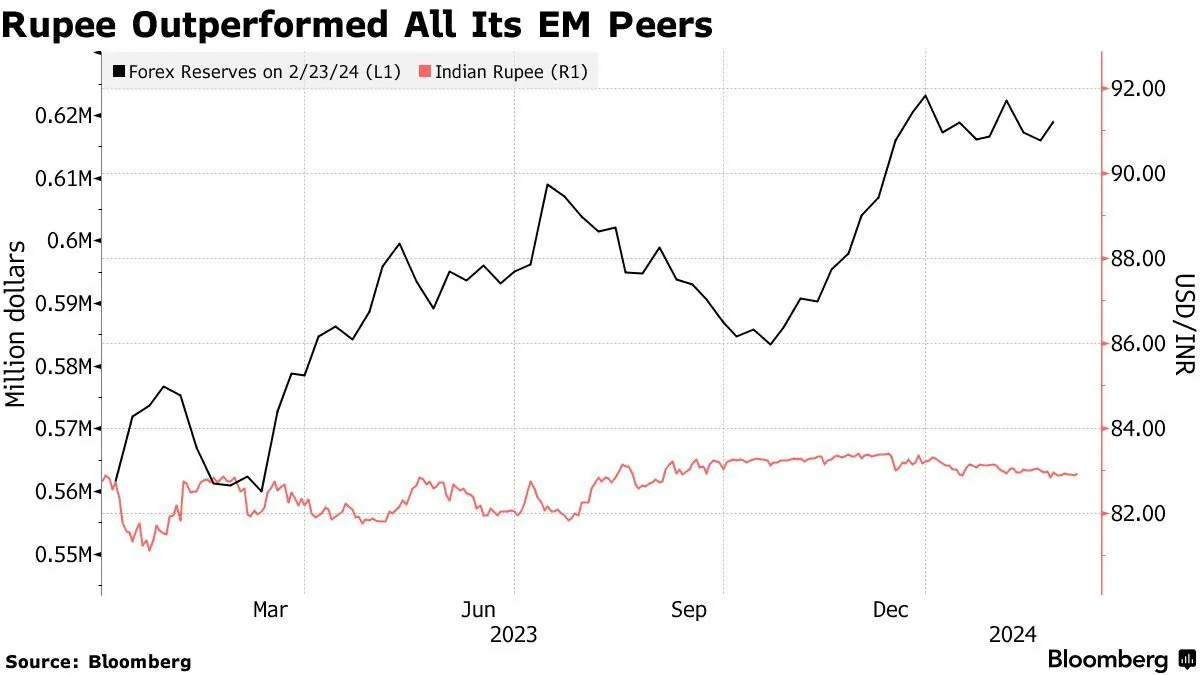
The RBI's management of forex reserves is crucial for maintaining economic stability. These reserves, capable of covering approximately 10 months of imports, provide a buffer against external shocks. The central bank's approach to monetary policy, which includes a flexible inflation targeting framework adopted in 2016, further underscores its commitment to economic stability.
As India navigates these financial challenges, the interplay between forex reserves, currency valuation, and economic policies remains a critical area of focus for policymakers and market observers alike.


































