Russian Economy Surges Despite Sanctions, Raising Overheating Concerns
Russia's economy shows robust growth across sectors, with record-low unemployment. Officials hint at a brighter outlook, but signs of overheating emerge amid Western sanctions and the ongoing conflict in Ukraine.
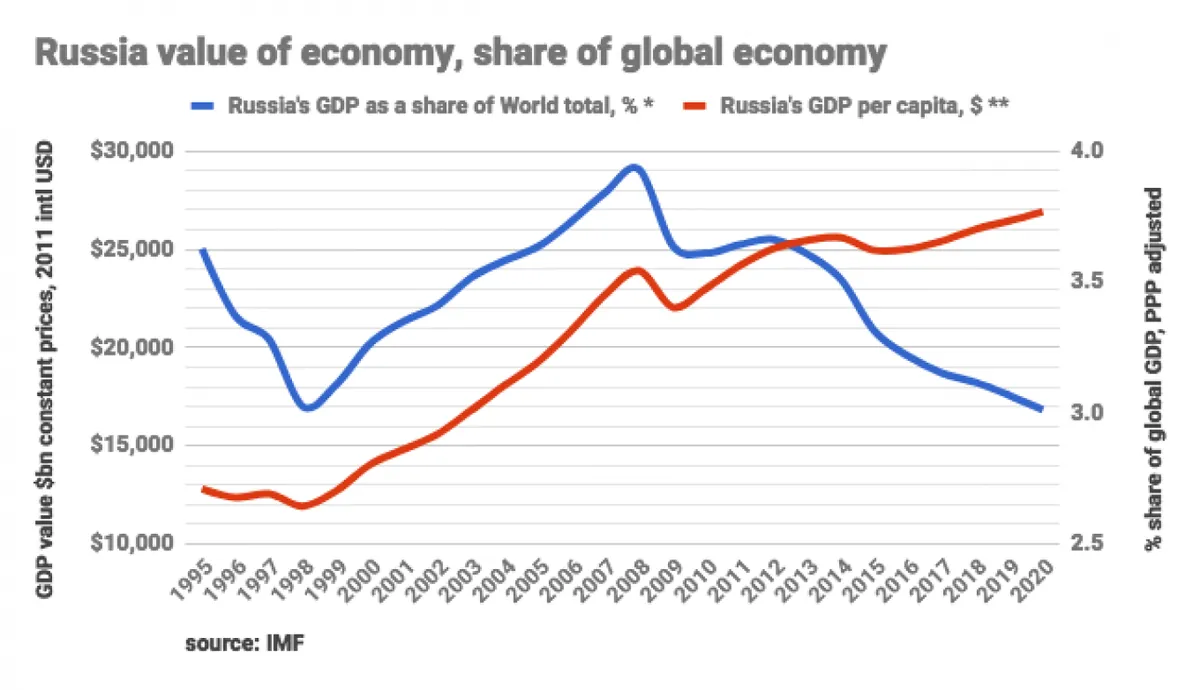
The Russian economy has demonstrated remarkable resilience and growth across various sectors, defying Western sanctions imposed due to the ongoing conflict in Ukraine. Recent data reveals a surge in industrial output and GDP growth, coupled with record-low unemployment rates, prompting officials to express optimism about the country's economic outlook for 2024.
Industrial production, primarily driven by military manufacturing, experienced a 3.3% increase in July 2024 compared to the previous month's 2.7% rise. Since the beginning of the year, industrial output has grown by 4.8%, surpassing the 3.1% growth observed during the same period in 2023. This robust performance highlights Russia's ability to adapt its industrial sector despite international pressures.
The preliminary estimate for GDP growth in the first half of 2024 stood at an impressive 4.6%, significantly outpacing the 1.8% growth recorded during the same period last year. Polina Kryuchkova, deputy economy minister, expressed confidence in even higher figures for the entire year, surpassing initial projections made in April.

Strong capital investment has been a key driver of this economic expansion. In the second quarter of 2024, investments rose by 8.3% year-on-year, reaching 8.44 trillion rubles ($92 billion). This follows a remarkable 14.5% growth in the first quarter, indicating sustained confidence in the Russian economy from both public and private sectors.
However, the rapid economic growth has raised concerns about potential overheating. The Russian Central Bank responded by raising its benchmark interest rate to 18% in July, the highest level in over two years. This move aims to curb inflation and address persistent labor shortages and wage growth, which are seen as primary indicators of an overheated economy.
Real wages in Russia have shown significant increases, with a 6.2% year-on-year rise in June 2024, following an 8.8% increase in May. Average nominal wages surged by 15.3% year-on-year, reaching 89,145 rubles per month. The wage growth is partly attributed to the high salaries offered to contract soldiers involved in the Ukraine conflict, which have set new benchmarks for worker expectations across various sectors.
Despite these positive indicators, Russia faces challenges in international trade. Imports fell by 9% in the first half of 2024, reflecting difficulties in international payments with major trading partners like China. This decline underscores the ongoing impact of Western economic sanctions on Russia's global economic interactions.
It's worth noting that Russia's economic performance is set against the backdrop of its vast natural resources and strategic global position. As the world's largest country by land area, Russia possesses the largest natural gas reserves globally and ranks as the third-largest oil producer. These factors contribute significantly to its economic resilience and ability to withstand external pressures.
The Russian labor market remains tight, with unemployment at a historically low level of 2.4% in July 2024. This figure represents approximately 1.9 million people out of work in a country with a highly educated workforce, where over 50% of adults hold tertiary education degrees.
As Russia navigates its economic course amidst geopolitical tensions, the country's membership in BRICS and its position as the 11th largest economy by nominal GDP underscore its significant role in the global economic landscape. The coming months will be crucial in determining whether Russia can maintain this growth trajectory while addressing the challenges of potential economic overheating and ongoing international sanctions.


































