US, Canada, and Finland Unite to Challenge China's Arctic Ambitions
The ICE Pact, a new trilateral agreement, aims to boost icebreaker production and counter China's growing influence in the Arctic. This strategic move addresses US shipbuilding decline and regional geopolitical challenges.
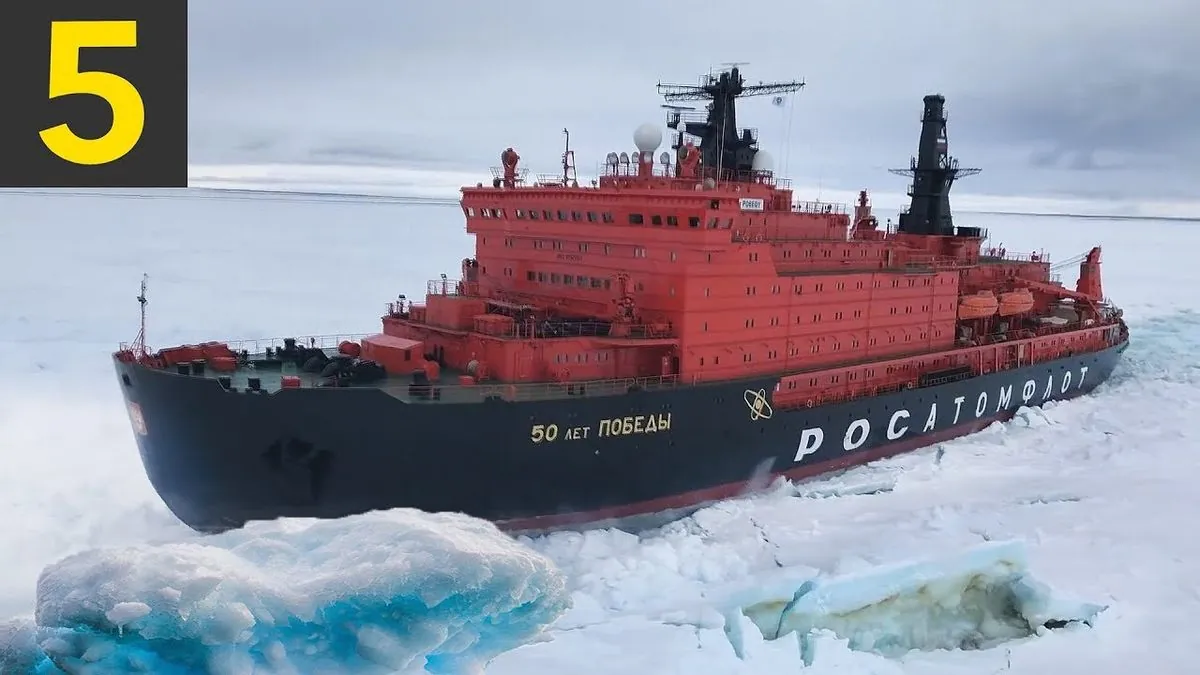

In a strategic move to address the declining US shipbuilding industry and counter China's growing Arctic influence, the United States, Canada, and Finland have formed the Icebreaker Collaboration Effort (ICE Pact). This trilateral agreement, announced during the NATO summit in Washington in July 2024, aims to revitalize icebreaker production among the three Arctic nations.
The ICE Pact emerges as a response to two critical challenges: the diminishing US shipbuilding capacity and the intensifying geopolitical competition in the Arctic region. These issues are intrinsically linked to China's expanding shipbuilding empire and its increasing presence in the Arctic.
China's dominance in global shipbuilding has become a significant concern for the United States. The Asian giant now accounts for over half of the world's production of civilian and merchant ships, utilizing dual-use shipyards that can construct both commercial vessels and warships. This practice has accelerated China's naval-industrial development, blurring the lines between civilian and defense sectors.
In response, the Biden administration has implemented policies to counter China's shipbuilding prowess. In April 2024, the White House launched an investigation into Beijing's non-market industrial practices in shipbuilding, which may lead to new tariffs on Chinese-built ships.
The Arctic's strategic importance has grown substantially due to melting sea ice, which has unlocked new sea lanes and access to natural resources. The US Department of Defense's Arctic Strategy, published in July 2024, identifies China's increased activities in the region as the top strategic challenge. NATO has also taken a firmer stance against China's northern advances in recent years.
"The increased competition and militarization in the Arctic region, especially by Russia and China, is concerning. ... We cannot be naïve and ignore the potentially nefarious intentions of some actors in the region. We must remain vigilant and prepare for the unexpected."
The ICE Pact focuses on icebreaker production due to the critical role these vessels play in Arctic operations. Currently, there is a significant disparity in icebreaker fleets among Arctic nations. Russia operates over 40 ice-class vessels, including nuclear-powered icebreakers, while China has four in operation with plans for more. In contrast, the United States has only two aging icebreakers in need of upgrades.
The agreement aims to leverage the combined industrial capacity and technological expertise of the three nations. Finland, a global leader in icebreaker design and production, will play a crucial role in the pact. Canadian companies are also powerhouses in this field, while the United States can contribute its high-tech ecosystem for developing next-generation technologies.

However, the ICE Pact faces potential obstacles. Some Finnish firms involved in icebreaker design and production have significant operations in China, raising concerns about technology transfer. Additionally, an ongoing dispute between the United States and Canada over Arctic waters jurisdiction along the Northwest Passage could complicate cooperation.
Despite these challenges, the ICE Pact represents a creative first step in addressing China's shipbuilding dominance and maintaining NATO's Arctic influence. By fostering collaboration and investment in icebreaker production, the agreement aims to safeguard peace and security in this increasingly important frontier.