Biden Administration Mulls Stricter Asylum Rules Amid Border Concerns
U.S. officials consider extending the period for lower illegal border crossings before lifting asylum restrictions. The move aims to maintain reduced migration levels ahead of the 2024 election.

The Biden administration is contemplating a modification to its asylum policy, potentially extending the duration required for reduced illegal border crossings before lifting current restrictions. This consideration comes as immigration remains a pivotal issue in the lead-up to the November 5, 2024, U.S. election.
On June 5, 2023, President Joe Biden implemented an asylum ban, significantly limiting asylum eligibility for those who crossed the southern border illegally. This measure, part of the administration's efforts to manage migration, was introduced after Congress failed to pass a bipartisan border security bill earlier that year.
The existing policy stipulates that the ban can be lifted if illegal crossings at the U.S.-Mexico border remain below an average of 1,500 per day for one week, followed by a two-week waiting period. However, officials are now discussing extending this threshold period to several weeks, aiming to ensure a more sustained reduction in crossings.
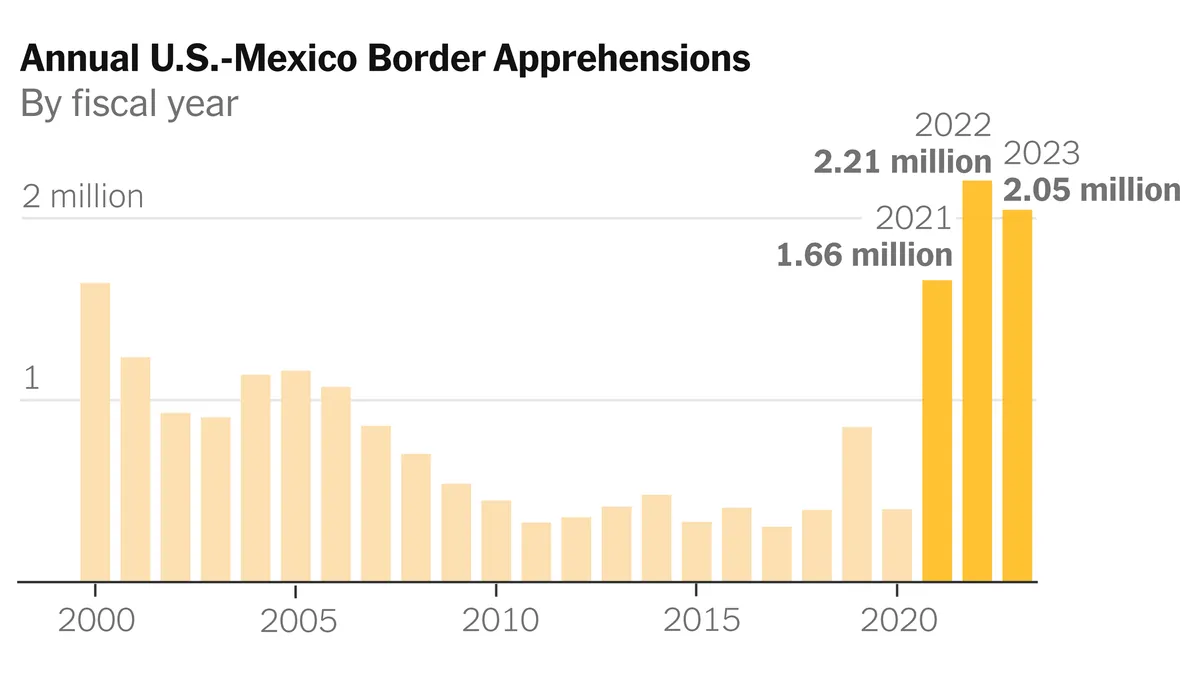
The impact of the current policy has been notable. In July 2023, approximately 56,000 migrants were apprehended crossing the border illegally, a significant decrease from 118,000 in May 2023. Despite this reduction, the daily average in July still exceeded the 1,500 threshold, with about 1,820 apprehensions per day.
It's worth noting that the U.S.-Mexico border, stretching approximately 1,954 miles (3,145 km), has been a focal point of immigration debates for decades. The Border Patrol, established in 1924, has been at the forefront of these efforts, with its role evolving significantly over time.
The asylum ban, currently classified as an "interim final rule" by the Department of Homeland Security and the Justice Department, is still pending finalization. This classification allows for potential adjustments based on public feedback and changing circumstances.
Immigration policy continues to be a contentious issue in American politics. Donald Trump, the Republican presidential candidate, has pledged mass deportations if re-elected. Conversely, Vice President Kamala Harris, representing the Democratic ticket, has criticized Trump's opposition to the failed bipartisan border security bill.
The ongoing debate reflects the complex nature of U.S. immigration policy. Since 1960, the United States has been the world's top destination for international migrants, with approximately 45 million immigrants as of 2023. The country admits roughly 1 million legal permanent residents annually, while also grappling with challenges related to undocumented immigration.
As the administration considers these policy adjustments, it's crucial to remember that immigration laws and policies have far-reaching effects. For instance, the Supreme Court's 1982 ruling in Plyler v. Doe established that undocumented children have the right to public education, highlighting the multifaceted nature of immigration issues in the U.S.
"The restrictions were needed after Republicans rejected the Senate bill and that migrants could use new Biden-era pathways to enter the U.S. legally."
As the 2024 election approaches, the ongoing discussions about asylum policy underscore the continuing significance of immigration as a key political and social issue in the United States.


































