Argentina's Economy Faces Continued Recession Amid Austerity Measures
Argentina's economy likely contracted 1.4% in Q2 2023, marking the fifth consecutive decline. President Milei's austerity measures aim to combat inflation and reduce fiscal deficit, despite economic challenges.

Argentina's economy continues to face challenges as it likely experienced a 1.4% contraction in the second quarter of 2023 compared to the previous year, according to a recent Reuters poll. This marks the fifth consecutive decline, highlighting the deepening recession under President Javier Milei's stringent austerity program.
The projected decline follows a more significant 5.1% year-over-year contraction in the first quarter of 2023. Official data confirming these figures is expected to be released on September 20, 2023. Milei's cost-cutting measures, while aimed at addressing long-standing economic issues, have had a noticeable impact on economic activity, leading to increased poverty and unemployment rates.
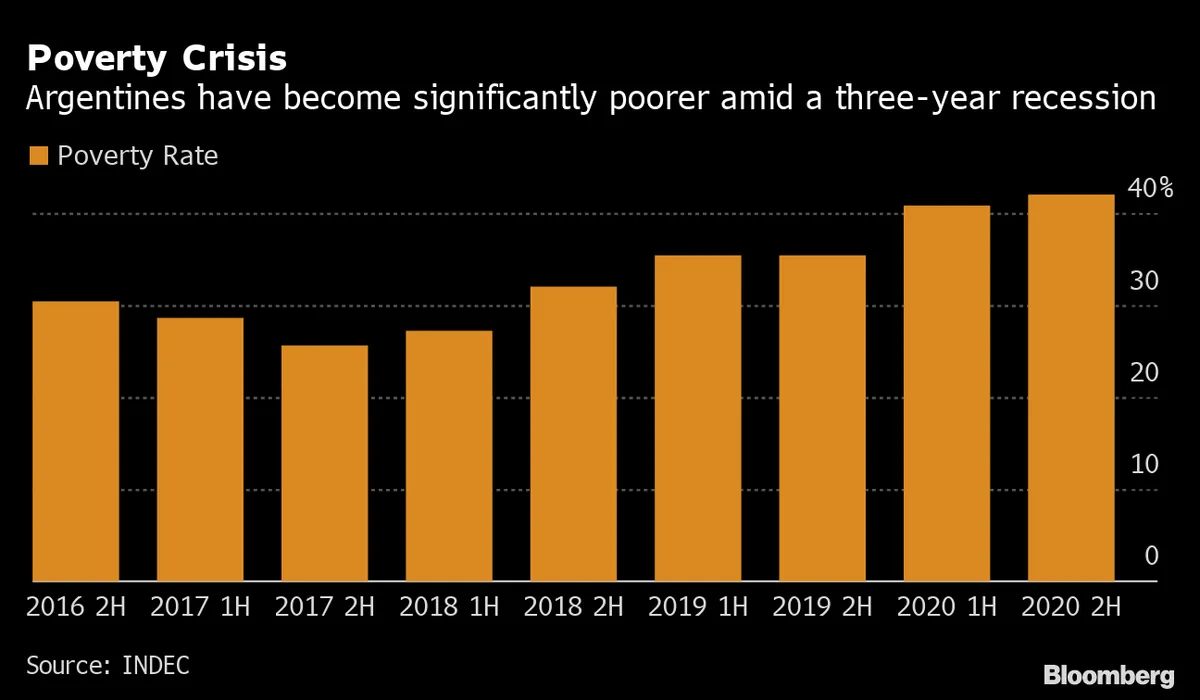
The government maintains that these austere policies are necessary to combat the country's persistent economic challenges. Argentina, once among the world's wealthiest nations in the early 20th century, has faced numerous economic crises since the 1980s, including multiple sovereign debt defaults. The current administration's primary objectives include:
- Reining in triple-digit inflation
- Rebuilding depleted foreign reserves
- Reversing years of deep fiscal deficits
Despite the ongoing recession, some analysts see potential signs of recovery. Marcelo Rojas, an economic expert, suggests that while the country remains in recession, there are indications that the economic downturn may be approaching its nadir. Rojas emphasizes the need for new capital investment to stimulate growth, stating, "GDP has a lot of room to grow, but new capital will be needed to generate momentum."
The Argentine economy's performance varies significantly across sectors. The agricultural sector, which accounts for about 10% of the country's GDP, has shown resilience along with the energy industry, particularly in the Vaca Muerta shale region – one of the world's largest unconventional oil and gas reserves. However, construction and consumer spending remain weak.
Pablo Besmedrisnik, an economist at consultancy VDC, notes the contrasting sectoral performance: "The agricultural sector, energy and mining show solid recovery rates. In contrast, construction, financial intermediation and trade show significant declines."
On the inflation front, there has been some improvement. Monthly inflation rates have decreased from 25% in December 2023 to approximately 4% in recent months. However, the annualized inflation rate remains above 250%, the highest globally. The government aims to significantly reduce this figure by the end of the year.
"We are committed to bringing down inflation to single digits by implementing necessary fiscal and monetary measures, despite short-term economic challenges."
Looking ahead, Milei's administration has set an ambitious target of 5% GDP growth for 2025, as outlined in the recently presented budget. This goal reflects the government's optimism about the long-term effects of its economic reforms.
Argentina's economic situation remains complex, with a significant informal economy estimated at 25-35% of GDP and a history of implementing various economic models. As the country navigates these challenges, its highly educated workforce and strong agricultural and wine industries may provide foundations for future growth.
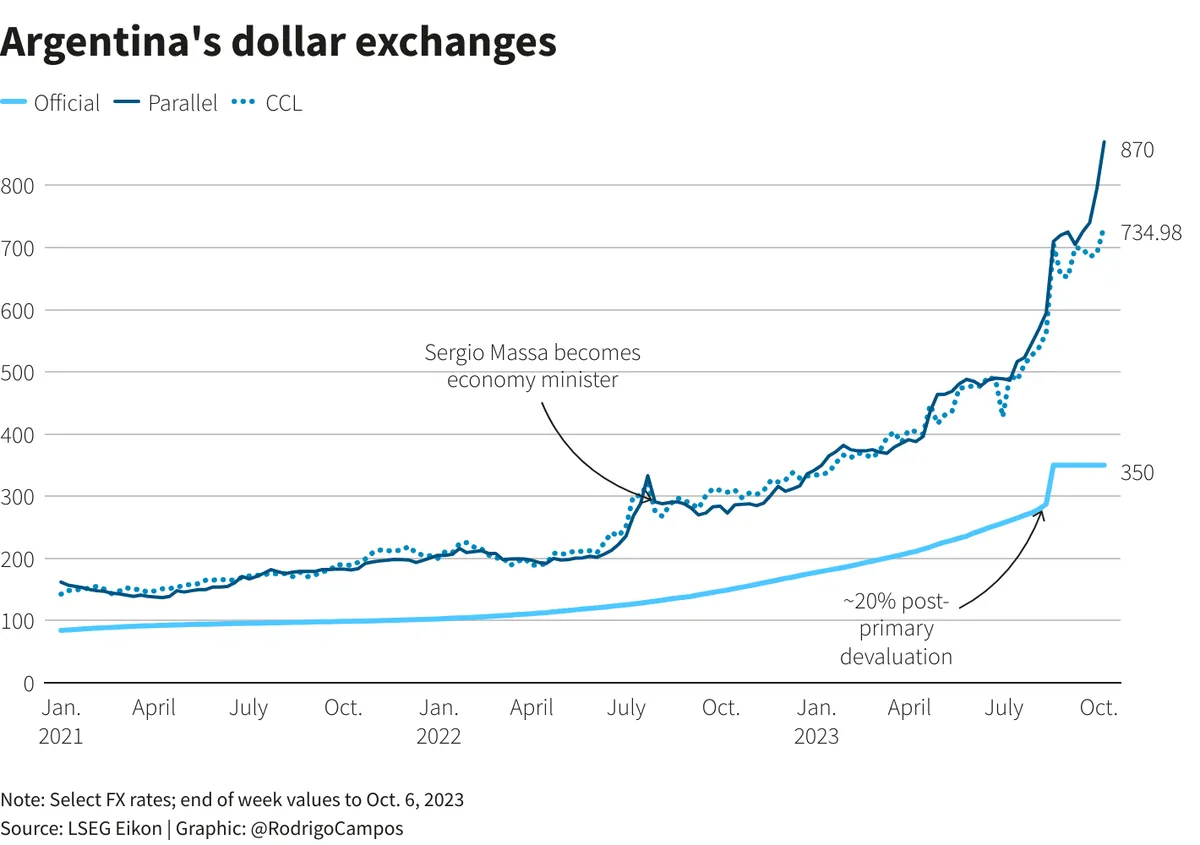
As Argentina continues its efforts to stabilize its economy and attract new investments, the coming months will be crucial in determining whether the current austerity measures will yield the desired results in terms of inflation control and economic recovery.


































