Digital Twins: Balancing Innovation with Privacy and Ethical Concerns
Digital twin technology offers immense benefits across industries, but raises privacy, security, and ethical concerns. Developers must navigate these challenges to responsibly harness the potential of virtual replicas.

Digital twin technology, a concept first introduced by Dr. Michael Grieves in 2002, has gained significant traction across various industries. These virtual replicas of physical objects or systems offer numerous benefits, from improving medical procedures to enhancing city planning. However, as with any emerging technology, digital twins present a complex landscape of opportunities and challenges.
The global digital twin market is projected to reach $48.2 billion by 2026, highlighting the rapid adoption of this technology. Industries such as healthcare, manufacturing, and aerospace are leveraging digital twins to revolutionize their operations. For instance, digital twins can reduce maintenance costs by up to 30% in manufacturing and potentially save $100 billion annually in the U.S. healthcare sector alone.
Despite these promising prospects, digital twins face several hurdles in terms of privacy, security, and ethical considerations. Privacy laws, which emphasize data minimization and consent, may conflict with the data-intensive nature of digital twins. Developers must grapple with questions such as data retention periods and the feasibility of anonymization in digital twin environments.
Security concerns are equally pressing. The continuous influx of sensitive data from various sources, often transmitted via internet-connected devices, makes digital twins vulnerable to cyber threats. With ransomware attacks on the rise, ensuring robust security measures is paramount. Developers must adopt a "security by design" approach, not only for the digital twin itself but also for all connected technologies.
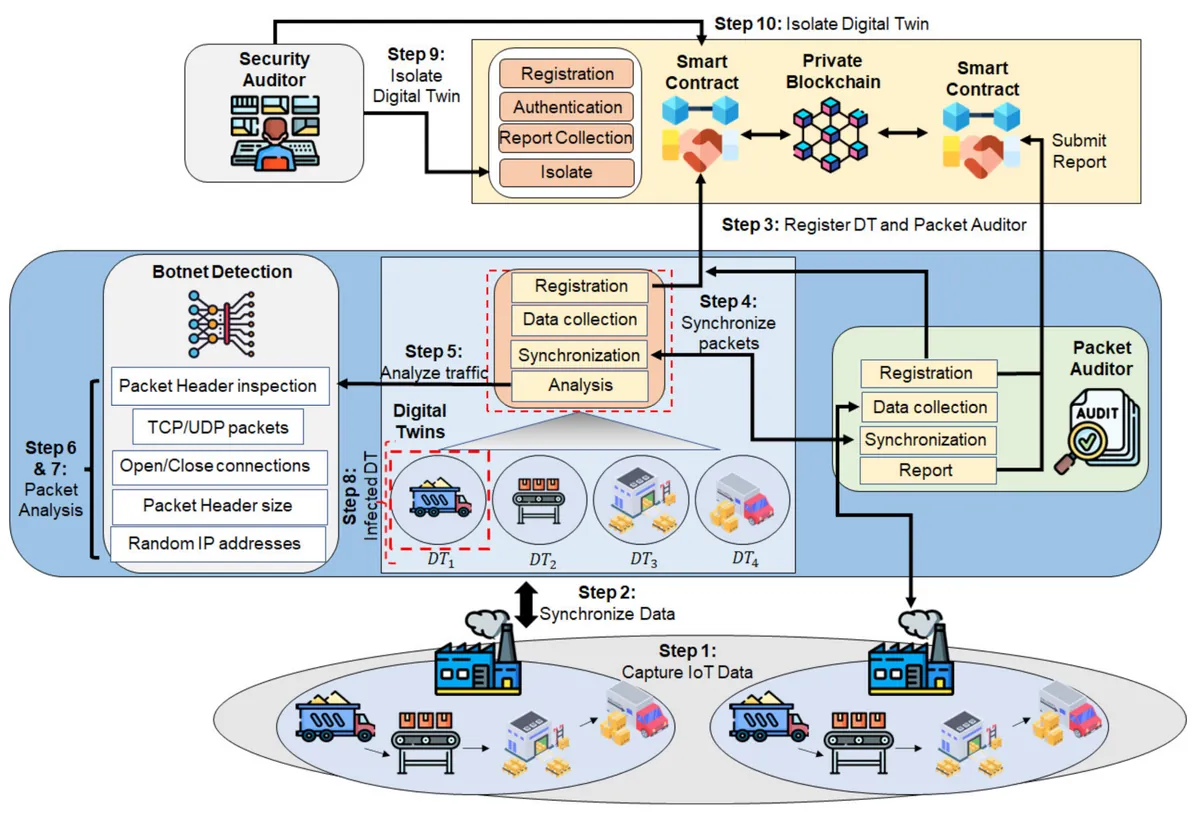
Ethical implications of digital twins are multifaceted. While the individualized nature of digital twins offers unprecedented insights, it also raises questions about data ownership, consent, and the potential for misuse. In the medical field, for example, the discovery of unforeseen health risks through a digital twin could create complex ethical dilemmas regarding patient notification and broader public health considerations.
The first digital twin of an entire city, created for Singapore in 2018, demonstrates the technology's potential in urban planning. Such applications can improve energy efficiency in buildings by up to 50% and help reduce carbon emissions in smart cities by up to 50%. However, these benefits must be balanced against privacy concerns and the risk of over-individualization.
As digital twin technology continues to evolve, it is crucial for developers, legal experts, and ethicists to collaborate in addressing these challenges. The integration of digital twins with other emerging technologies, such as artificial intelligence and the Internet of Things, further underscores the need for a comprehensive approach to innovation.
"There is no doubt that digital twin technology could revolutionize research into the human body, as well as manufacturing, design, city planning, and a host of other conceivable use cases. With that in mind, digital twin developers must consider where general principles of ethics, privacy, and security would benefit the innovative process."
In conclusion, while digital twins offer immense potential to transform industries and improve quality of life, their development must be guided by robust ethical frameworks and stringent privacy and security measures. By addressing these concerns proactively, we can harness the full potential of digital twins while safeguarding individual rights and societal interests.


































