Gabon Reports First Mpox Case as Global Health Concerns Rise
Gabon has confirmed its first mpox case in a traveler from Uganda. The World Health Organization has declared the disease a global health emergency, with concerns about a new variant's transmission speed.

Gabon has reported its first case of mpox, marking a significant development in the spread of this viral infection. The announcement came from the Gabonese health ministry, though the specific variant involved was not disclosed.
World Health Organization (WHO) has elevated mpox to the status of a global public health emergency. This decision was prompted by the outbreak in the Democratic Republic of Congo expanding to neighboring nations and the emergence of a new form of the virus, known as clade Ib, which has raised concerns about its rapid transmission rate.
The Gabonese health authorities officially confirmed the country's inaugural mpox case on August 22, 2024. The patient, a 30-year-old male, tested positive after returning from Uganda. He exhibited typical symptoms of the disease, including fever and characteristic skin lesions.
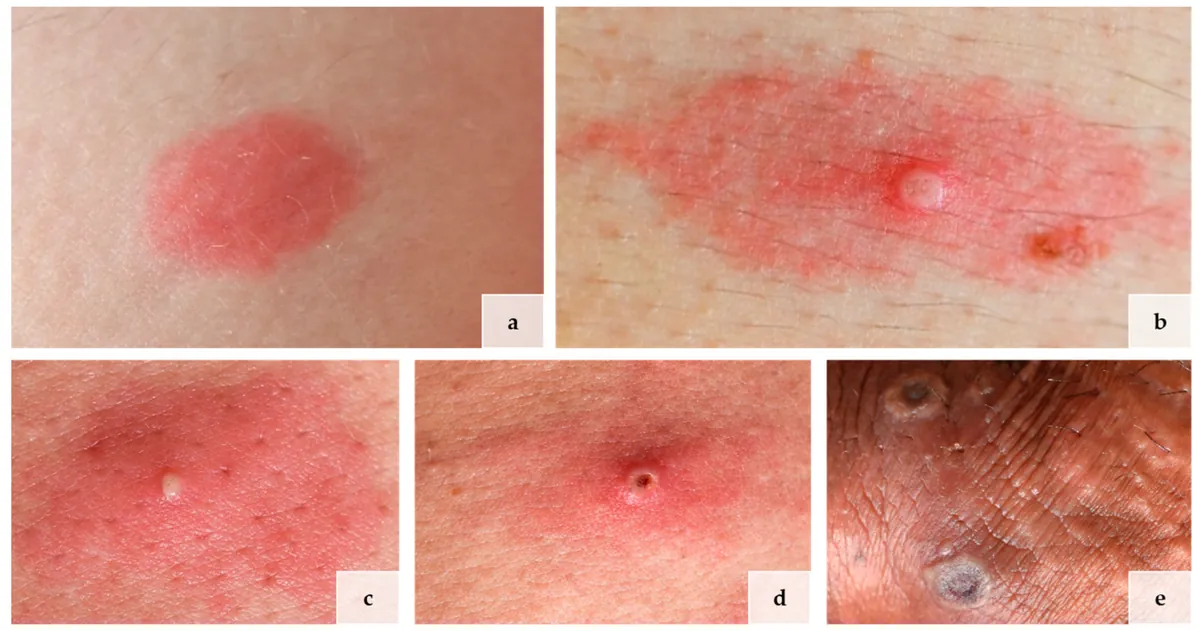
Mpox, formerly known as monkeypox, has been a focus of global health concerns since its discovery in 1958. The virus, part of the same family as smallpox, was first identified in humans in 1970 in the Democratic Republic of Congo. Typically found in central and west Africa, mpox has been spreading to non-endemic regions in recent years.
The disease is characterized by symptoms such as fever, rash, and swollen lymph nodes. It can be transmitted through close contact with infected animals or humans. The incubation period usually ranges from 7 to 14 days but can extend up to 21 days.
There are two known clades of the mpox virus: the Congo Basin clade and the West African clade. The fatality rate can vary significantly, ranging from 0% to 11%, depending on the specific clade involved. While vaccines developed for smallpox offer some protection against mpox, the recent global outbreak has highlighted the need for increased vigilance and preventive measures.
Gabon's geographical location on the west coast of Central Africa, bordering countries like Equatorial Guinea, Cameroon, and the Republic of Congo, makes this case particularly noteworthy. The patient's travel history from Uganda, a country that has experienced several mpox outbreaks in the past, underscores the importance of international cooperation in disease surveillance and control.
As health authorities worldwide continue to monitor the situation, this case in Gabon serves as a reminder of the ongoing challenges in global health security and the need for robust public health systems to detect and respond to emerging infectious diseases promptly.
"The ongoing mpox outbreak is a stark reminder of the interconnectedness of global health. We must remain vigilant and work together to contain its spread and protect vulnerable populations."


































