Middle East Dynamics: 5 Key Changes Post-Israel-Hamas Conflict
Analysis of potential shifts in Middle East dynamics following a hypothetical Israel-Hamas cease-fire. Explores changes in regional stability, governance, and international relations.
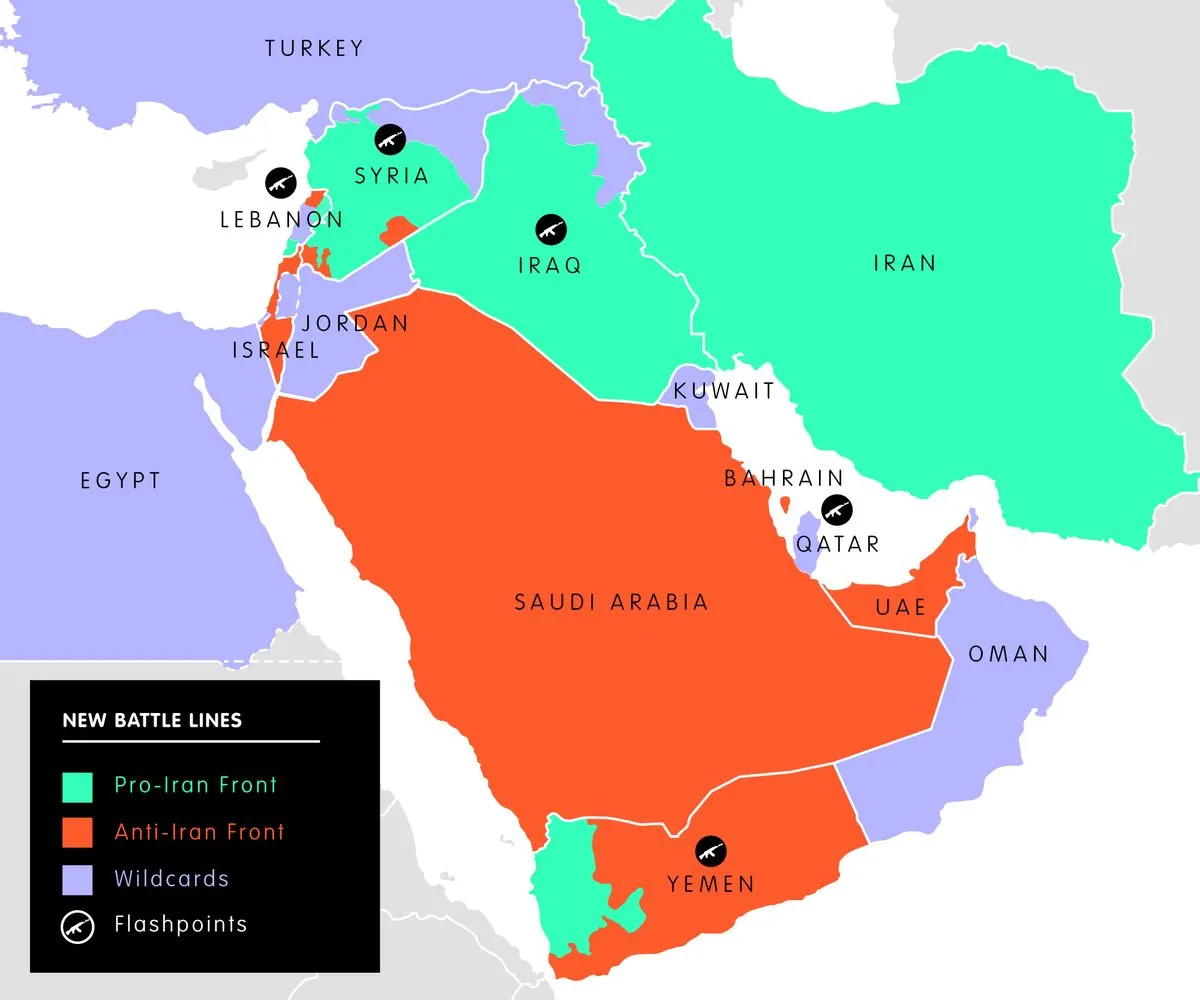
The potential cessation of hostilities between Israel and Hamas could bring temporary relief to the region, but it's unlikely to restore the pre-conflict status quo. As we approach the one-year mark since the October 7, 2023 attack, it's crucial to examine the lasting impacts on Middle Eastern dynamics.
Five significant changes are likely to shape the region's future:
Heightened Israeli vigilance: Israel's tolerance for perceived threats from Hamas, Hezbollah, Iran, or other adversaries is expected to diminish significantly. The October 7 attack exposed vulnerabilities in Israeli intelligence and military preparedness, shattering long-held assumptions about deterrence and security. This may lead to more preemptive actions and a lower threshold for what constitutes a provocation.
Further marginalization of the Palestinian Authority: The Palestinian Authority (PA), established in 1994 as part of the Oslo Accords, faces an even steeper decline in relevance and effectiveness. Support for Mahmoud Abbas and his Fatah party has plummeted among Palestinians, while Israel's trust in the PA as a security partner has eroded. This power vacuum in the West Bank, which has been under Israeli occupation since 1967, complicates prospects for stability and future negotiations.
Potential new alliances in conflicts: The involvement of Hezbollah, Iran, and the Houthis in the recent conflict may embolden Hamas to expect support in future confrontations. This dynamic could escalate minor skirmishes into broader regional conflicts, even if unintended.
Gaza's uncertain future: The Gaza Strip, under Hamas control since 2007, faces the risk of becoming a failed state. Proposals for post-conflict governance, ranging from PA control to international peacekeeping forces, seem unfeasible. The likely outcome is a fragmented territory with pockets of stability amid ongoing low-level insurgency and humanitarian crises.
Shifting U.S. involvement: While the United States may need to increase its engagement to maintain regional stability, there's a likelihood of reduced involvement. The complex challenges, including bolstering the PA and mediating Israeli-Palestinian relations, require significant diplomatic efforts that may not align with current U.S. priorities.

These potential shifts occur against a backdrop of historical complexities. The Israeli-Palestinian conflict has deep roots, with the two-state solution first proposed in the 1947 UN Partition Plan. Subsequent events, such as the founding of Hamas in 1987 during the First Intifada and the signing of the Oslo Accords in 1993 and 1995, have shaped the current landscape.
The region has seen moments of hope, such as the 2020 Abraham Accords normalizing relations between Israel and several Arab states. However, enduring challenges persist, including the Gaza blockade imposed by Israel and Egypt since 2007 and the ongoing Israeli occupation of the West Bank.
While the future remains uncertain, the risks of renewed conflict and regional instability are significant. As we hope for peace, it's crucial to prepare for potential challenges and work towards sustainable solutions in this complex geopolitical landscape.
"We must remain vigilant and prepared for any scenario. The security of our citizens is our top priority, and we will take all necessary measures to ensure it."
In conclusion, while a cease-fire would be a welcome development, it's essential to recognize that the Middle East's path forward will likely be fraught with new challenges and altered dynamics. The international community must remain engaged and proactive in addressing these evolving realities to foster long-term stability and peace in the region.


































