NHTSA Closes GM SUV Seat Belt Probe After Extended Warranty Offer
U.S. auto safety regulators conclude a five-year investigation into seat belt failures in certain GM SUVs. The probe's closure follows GM's extended warranty coverage addressing the issue.
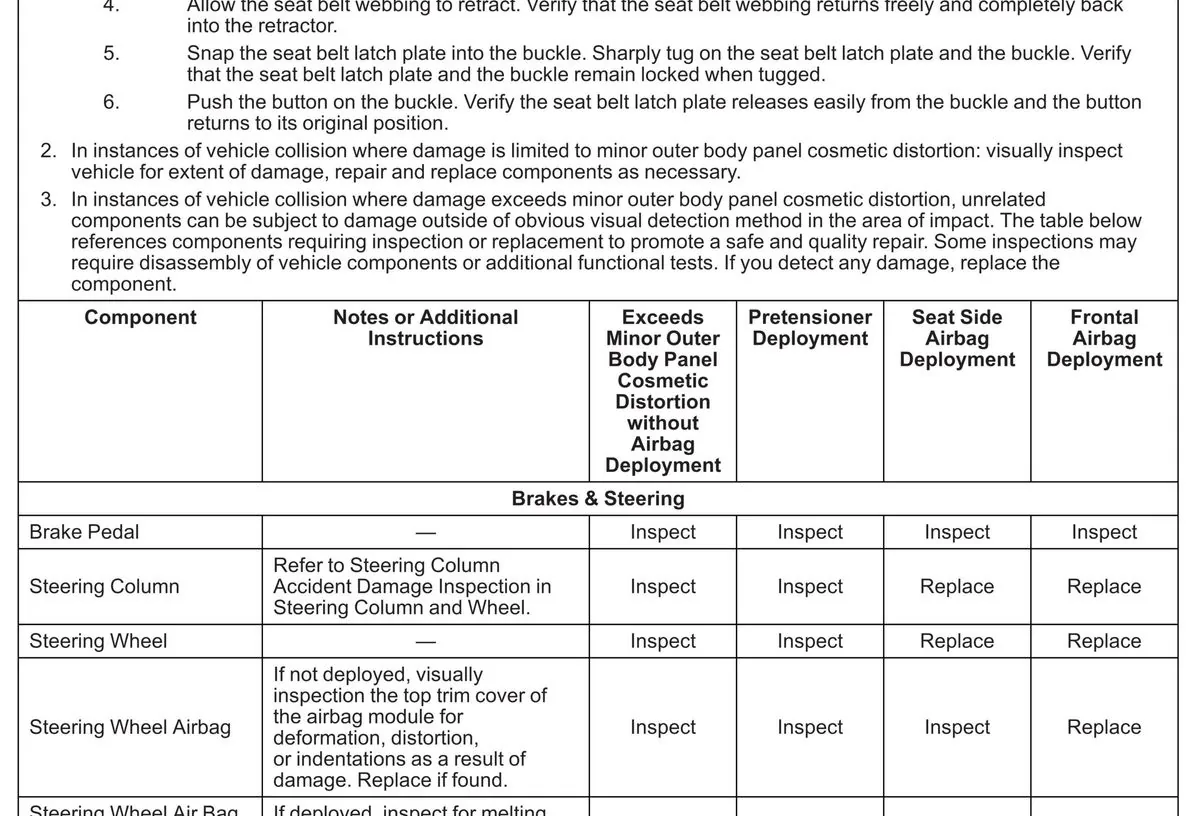
The National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) has concluded its five-year investigation into seat belt failures in specific General Motors (GM) sport utility vehicles (SUVs). This decision comes after GM implemented an extended warranty program to address the issue.
In 2014, GM initiated a recall affecting over 1.3 million midsize SUVs from the 2009-2014 model years. The recall encompassed the Chevrolet Traverse, Buick Enclave, GMC Acadia, and Saturn Outlook. The problem stemmed from a flexible steel cable connecting the seat belts to the front outside seats, which could potentially fail over time and compromise passenger safety during a crash.
Five years after the initial recall, in 2019, the NHTSA reopened the investigation following four reports of seat belt failures in SUVs that had undergone recall repairs. Fortunately, no injuries were reported in connection with these incidents.
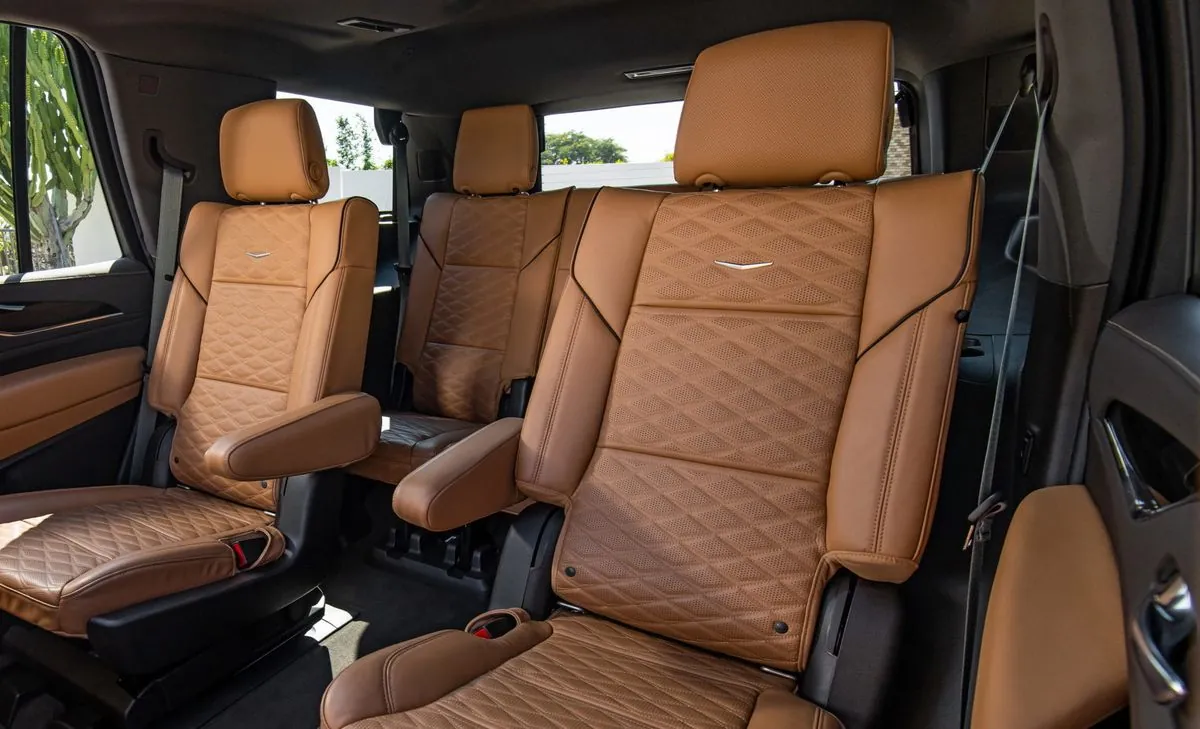

In response to the renewed concerns, GM extended the warranty coverage for the affected seat belt cables to 12 years or 180,000 miles from the initial sale date of the SUVs. This extension, implemented in June 2019, allowed technicians to inspect the driver's seat belt cable for damage to its protective sleeve. If damage was detected, the cable would be replaced and relocated to mitigate future issues.
The NHTSA's decision to close the investigation was based on three key factors: the high ability to detect the problem, the low rate of occurrence, and the additional warranty coverage provided by GM.
It's worth noting that seat belt technology has come a long way since its invention by Swedish engineer Nils Bohlin in 1959. The first U.S. federal law mandating seat belts in all new cars was passed in 1968, and pretensioners were introduced in the 1980s to further enhance safety.
The automotive industry, heavily regulated in terms of safety standards, often faces challenges related to recalls. GM, founded in 1908, has encountered several high-profile recalls throughout its history, including the ignition switch recall in 2014.
The NHTSA, established in 1970, plays a crucial role in ensuring vehicle safety. It has the authority to issue safety standards and require manufacturers to recall vehicles with safety-related defects. This recent case demonstrates the ongoing collaboration between regulatory agencies and automakers to address and resolve safety concerns in the automotive industry.


































