Pakistan Seeks $4 Billion from Middle East Banks, IMF Talks Progress
Pakistan's central bank chief outlines plans to secure $4 billion from Middle Eastern banks and progress on IMF bailout talks. The country aims to address financing needs and focus on economic growth.

Jameel Ahmad, Governor of the State Bank of Pakistan, has revealed plans to secure up to $4 billion in funding from Middle Eastern commercial banks by the next fiscal year. This initiative aims to address Pakistan's external financing requirements and stabilize the country's economic situation.
In an exclusive interview, Ahmad disclosed that Pakistan is in the advanced stages of obtaining an additional $2 billion in external financing. This funding is crucial for the approval of a $7 billion bailout program from the International Monetary Fund (IMF). The agreement between Pakistan and the IMF, reached in July 2024, is subject to approval from the IMF's executive board and confirmation of necessary financing assurances from Pakistan's development and bilateral partners.
Pakistan, the world's fifth-most populous country, has faced recurring balance of payments crises due to structural economic issues. Since joining the IMF in 1950, Pakistan has received 22 bailouts, highlighting the country's ongoing economic challenges.
Ahmad expressed confidence that Pakistan's gross financing needs would be met smoothly in the coming years. He stated, "Pakistan's external gross financing needs have been declining in the past few years." The central bank governor expects the ratio of gross financing needs to GDP to be lower than the 5.5% level projected by the IMF in its May 2024 report.
Regarding monetary policy, Ahmad noted that recent interest rate cuts have had the desired effect on inflation and the current account. Pakistan's annual consumer price index inflation stood at 11.1% in July 2024, a significant decrease from the over 30% levels seen in 2023. The central bank has reduced interest rates from a historic high of 22% to 19.5% in two consecutive meetings.
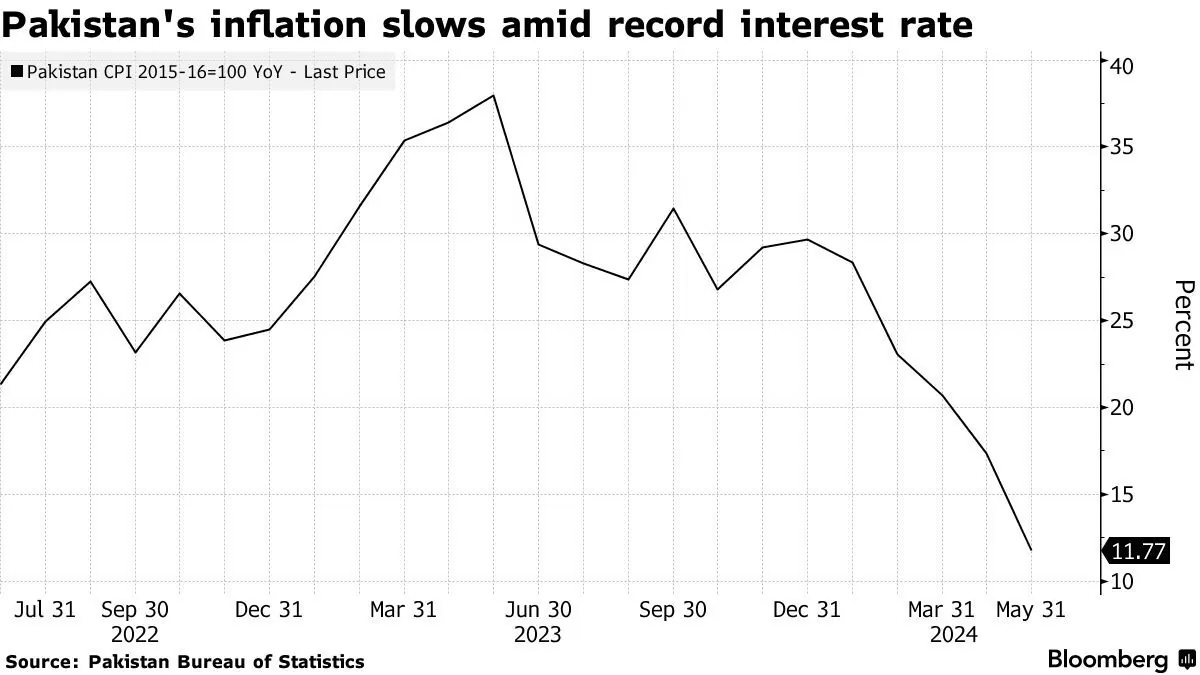
The State Bank of Pakistan, established in 1948 shortly after the country's independence, plays a crucial role in managing the nation's monetary policy. Ahmad emphasized that future rate decisions would be based on careful review of economic developments, with the next monetary policy meeting scheduled for September 12, 2024.
Reflecting on his first year in office, Ahmad acknowledged the challenges faced, particularly the acute balance of payments crisis in 2023 when central bank reserves could only cover a month of imports. However, he stated, "Now everything is under control from an external account management perspective."
Looking ahead, the central bank aims to focus on growth, digitalization, and financial inclusion. These priorities align with Pakistan's efforts to address its economic challenges, including a literacy rate of around 60% and an informal economy estimated at 35% of GDP.
"Those are also equally important for job creation and other socioeconomic issues. Our mandate is to ensure price and financial stability before shifting focus to growth."
Pakistan's economy heavily relies on textile exports, accounting for about 60% of total exports. The country has been implementing various initiatives to promote economic growth, including the development of special economic zones to attract foreign investment and exploring renewable energy options such as solar and wind power.
As Pakistan navigates its economic challenges, the success of these funding initiatives and the IMF bailout program will be crucial in determining the country's financial stability and future growth prospects.


































