African Nations Lose 5% GDP Annually Due to Climate Change Impact
African countries face significant economic losses from climate change, despite low emissions. A new report highlights the continent's vulnerability and the urgent need for adaptation measures.
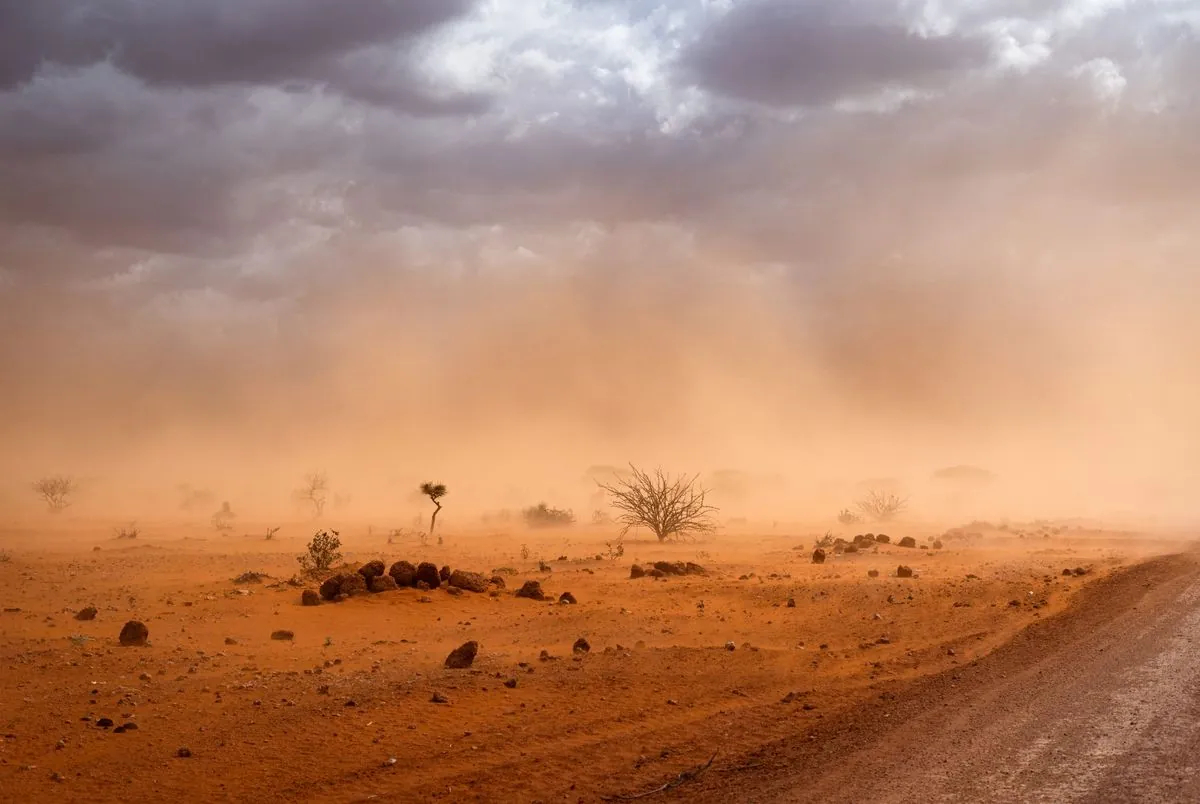

African nations are experiencing substantial economic losses due to the escalating impacts of climate change, according to a recent report by the World Meteorological Organization (WMO). The study reveals that these countries are forfeiting up to 5% of their Gross Domestic Product (GDP) annually, a figure that surpasses global averages.
Celeste Saulo, WMO Secretary-General, emphasized that Africa has witnessed a warming trend over the past six decades, outpacing the global average. This accelerated warming is affecting various sectors, including food security, public health, and regional stability.
Despite contributing less than 10% to global greenhouse gas emissions, Africa remains the most susceptible region to extreme weather events. The continent's vulnerability is exacerbated by its unique geographical features, including the world's largest desert, the Sahara, covering 31% of its land area, and the second-largest rainforest, the Congo Basin.
The report, focusing on 2023 - one of Africa's three hottest years on record - urges governments to invest in early warning systems and meteorological services. Without adequate measures, projections indicate that by 2030, approximately 118 million Africans could be exposed to droughts, floods, and extreme heat.
The financial burden of adapting to these climate challenges is substantial. For sub-Saharan Africa, adaptation costs are estimated to range between $30-50 billion annually over the next decade. This is particularly concerning for a continent that is home to some of the world's fastest-growing economies and has the highest solar irradiation levels globally, presenting both challenges and opportunities for sustainable development.
Recent extreme weather events have already had devastating consequences. Between September and October 2023, floods affected approximately 300,000 people across West Africa. Concurrently, Zambia experienced its worst drought in 40 years, impacting nearly 6 million individuals.
The pattern of extreme weather continues in 2024. The United Nations reports that flooding in the Sahel region has affected over 716,000 people this year alone. In Mali, authorities recently declared a national disaster due to floods impacting 47,000 people since the rainy season began.
These climate-related challenges are particularly pressing for Africa, which boasts the world's youngest population and is considered the birthplace of human species. The continent's rich biodiversity, extensive mineral resources, and rapidly growing middle class underscore the urgent need for effective climate adaptation strategies to protect both its people and its economic potential.
As Africa grapples with these environmental challenges, the international community must recognize the disproportionate impact of climate change on the continent and support its efforts to build resilience and sustainable development pathways.


































