NASA Extends Astronaut Mission as Helium Issues Plague Space Industry
NASA prolongs astronauts' ISS stay due to Boeing Starliner's helium leaks. SpaceX's Polaris Dawn mission faces delays. Industry grapples with persistent helium-related challenges in spacecraft and rockets.
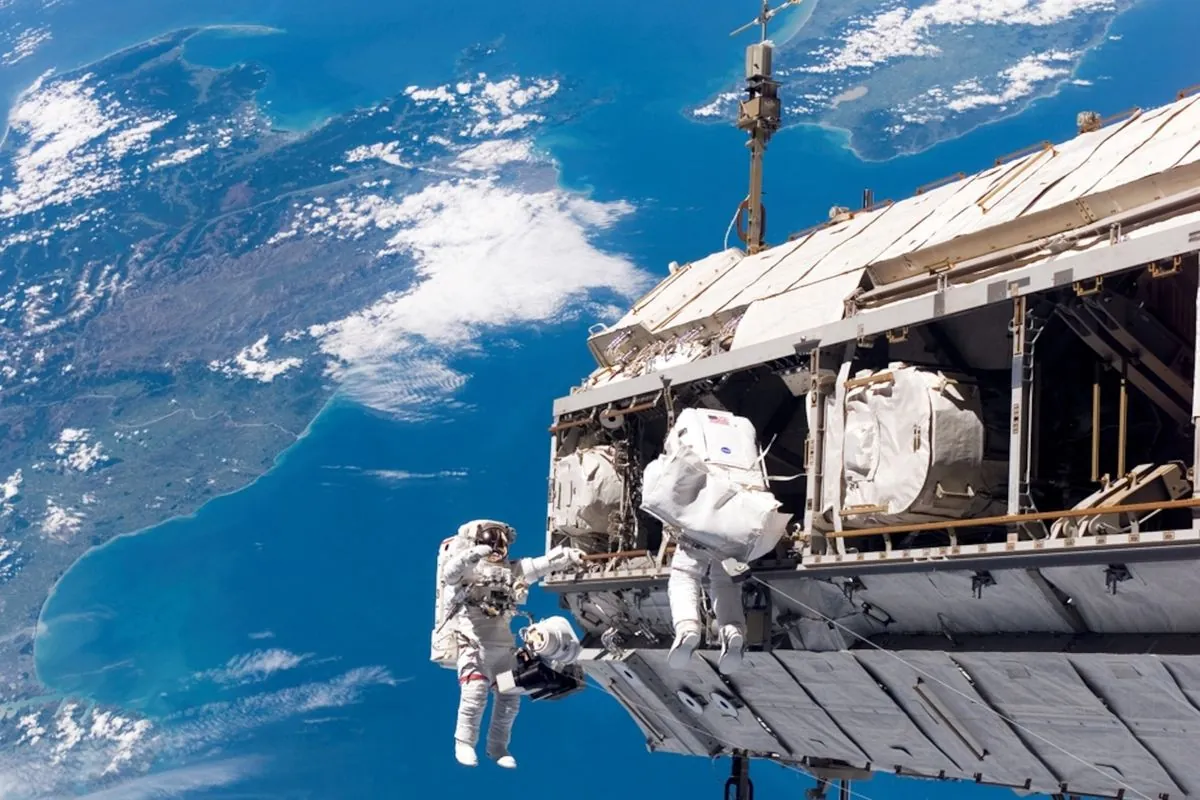

NASA has extended the stay of two astronauts aboard the International Space Station (ISS) due to issues with Boeing's Starliner spacecraft. The decision comes after the detection of helium leaks in the vehicle's propulsion system. This development highlights the ongoing challenges faced by the space industry in managing helium-related problems.
The Starliner spacecraft, which landed uncrewed in a New Mexico desert last Friday, has been plagued by technical difficulties. Concurrently, SpaceX's Polaris Dawn mission has experienced delays due to helium issues in ground equipment. These incidents underscore the critical role of helium in space technology and the complexities associated with its use.
Helium, the second most abundant element in the universe after hydrogen, plays a crucial role in spacecraft and rocket operations. Its unique properties make it invaluable for pressurizing fuel tanks and cooling systems. With an atomic number of 2, helium is exceptionally light, helping to reduce the overall weight of spacecraft. This is particularly important as rockets must achieve specific speeds and altitudes to reach and maintain orbit.
The gas's inert nature and extremely low boiling point (-268.9°C) allow it to remain in a gaseous state even in the frigid environments of space. These characteristics make helium ideal for use with cryogenic rocket fuels. However, its small atomic size also makes it prone to leaks, presenting a significant challenge for engineers and mission planners.
"Helium's propensity to escape through the tiniest gaps in seals and storage tanks is a constant concern in spacecraft design. While this property allows us to detect potential faults easily, it also necessitates extremely precise engineering and rigorous testing procedures."
The frequency of helium-related issues across various space missions has highlighted the need for innovation in valve design and more precise tightening mechanisms. Past missions affected by helium leaks include India's Chandrayaan 2 and the European Space Agency's Ariane 5.
Some alternatives to helium are being explored in the industry. For instance, Europe's new Ariane 6 rocket has implemented a novel pressurization system that converts liquid oxygen and hydrogen propellants to gas for pressurization. However, this system encountered difficulties during the rocket's debut launch in July 2024, demonstrating that pressurization challenges persist even with alternative approaches.
As the space industry continues to evolve, addressing helium-related issues remains a priority. The extended stay of NASA astronauts on the ISS and the delay of the Polaris Dawn mission serve as reminders of the ongoing need for technological advancements in this critical area of space exploration.


































