Fed's Rate Cut Signals: Global Impact and Powell's Political Acumen
Federal Reserve's anticipated interest rate reduction sparks discussions on consumer effects and global economic repercussions. Jerome Powell's leadership style marks a shift in central banking approach.

The Federal Reserve is poised to adjust its monetary policy, signaling a potential reduction in interest rates after years of increases aimed at curbing inflation. This shift comes in response to recent economic indicators suggesting a weakening labor market and looming recession risks in the United States.
The implications of this policy change extend beyond American borders, affecting global financial markets and economies worldwide. To understand the ramifications, it's crucial to examine the consumer impact, international consequences, and the leadership style of Fed Chair Jerome Powell.
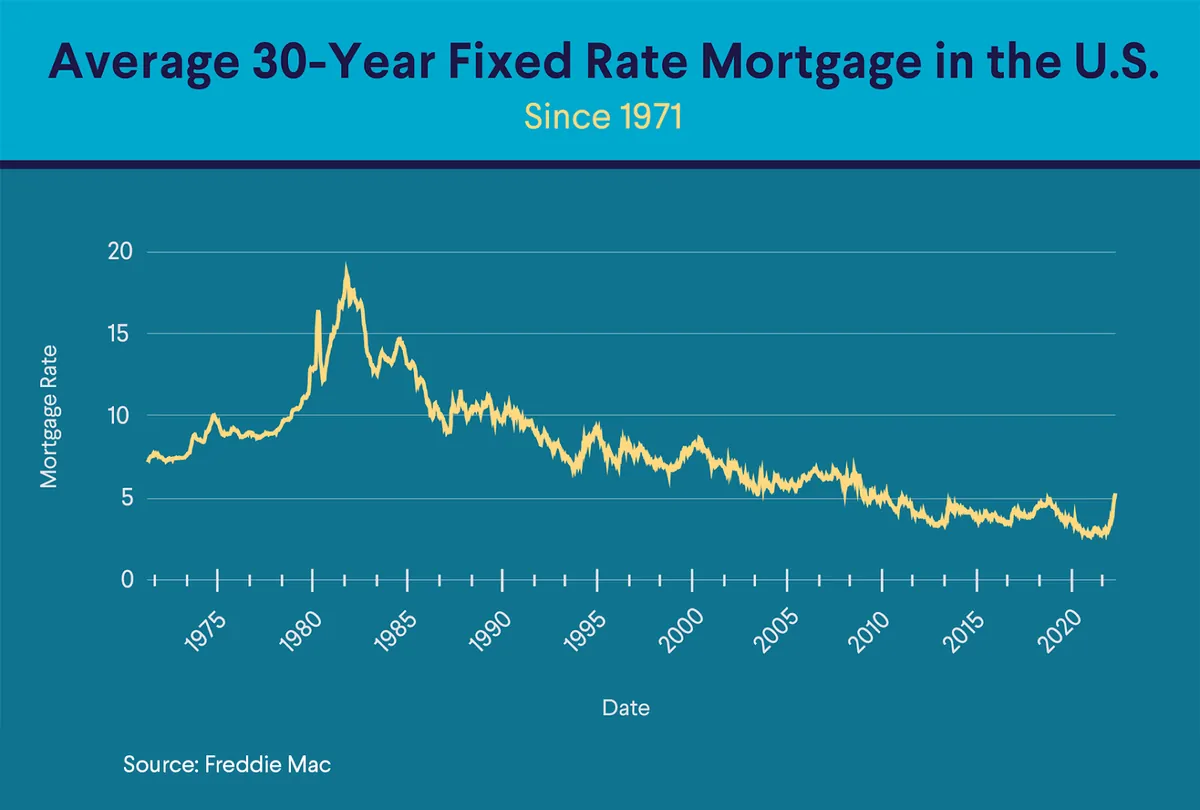
For consumers, the effects of lower interest rates may not be immediately apparent. Mortgage rates, currently hovering around 6%, could potentially decrease to a range of 4.5% to 5.5% if the trend continues. However, the transmission mechanism between Fed rates and consumer lending is complex, involving various factors such as banks' management of mortgage-backed securities portfolios.
The global impact of the recent high-interest rate period has been significant, particularly for developing nations. The Eurobond market, a crucial source of funding for emerging and low-income countries, experienced a 70% collapse in issuance from 2022 to 2023. This resulted in net outflows for many nations, exacerbating debt crises and political tensions in countries like Bolivia, Kenya, Sri Lanka, Argentina, and Pakistan.
"When we in the U.S. talk about a soft landing, we should check ourselves for a second and just consider for a moment the vast majority of humanity for whom this American interest rate hike delivered a really very, very painful blow."
Jerome Powell's leadership as Fed Chair marks a departure from his predecessors. Unlike the economist-technocrats of the past, Powell's background lies in banking and private finance. His approach emphasizes political acumen and congressional relationships, reflecting a shift in the role of central bankers.
This evolution in central banking leadership is not unique to the United States. Christine Lagarde's appointment as President of the European Central Bank in 2019 similarly reflects a trend towards leaders with strong political and legal backgrounds rather than purely economic expertise.
The changing nature of central banking leadership coincides with increasingly radical policy interventions, particularly in response to crises like the COVID-19 pandemic. Powell's ability to navigate political landscapes while implementing bold monetary policies highlights the delicate balance between economic management and political legitimacy that modern central bankers must strike.
As the Federal Reserve contemplates its next moves, the global economy watches closely. The interconnectedness of financial markets means that decisions made in Washington reverberate across the world, affecting everything from mortgage rates in American suburbs to debt sustainability in developing nations.


































