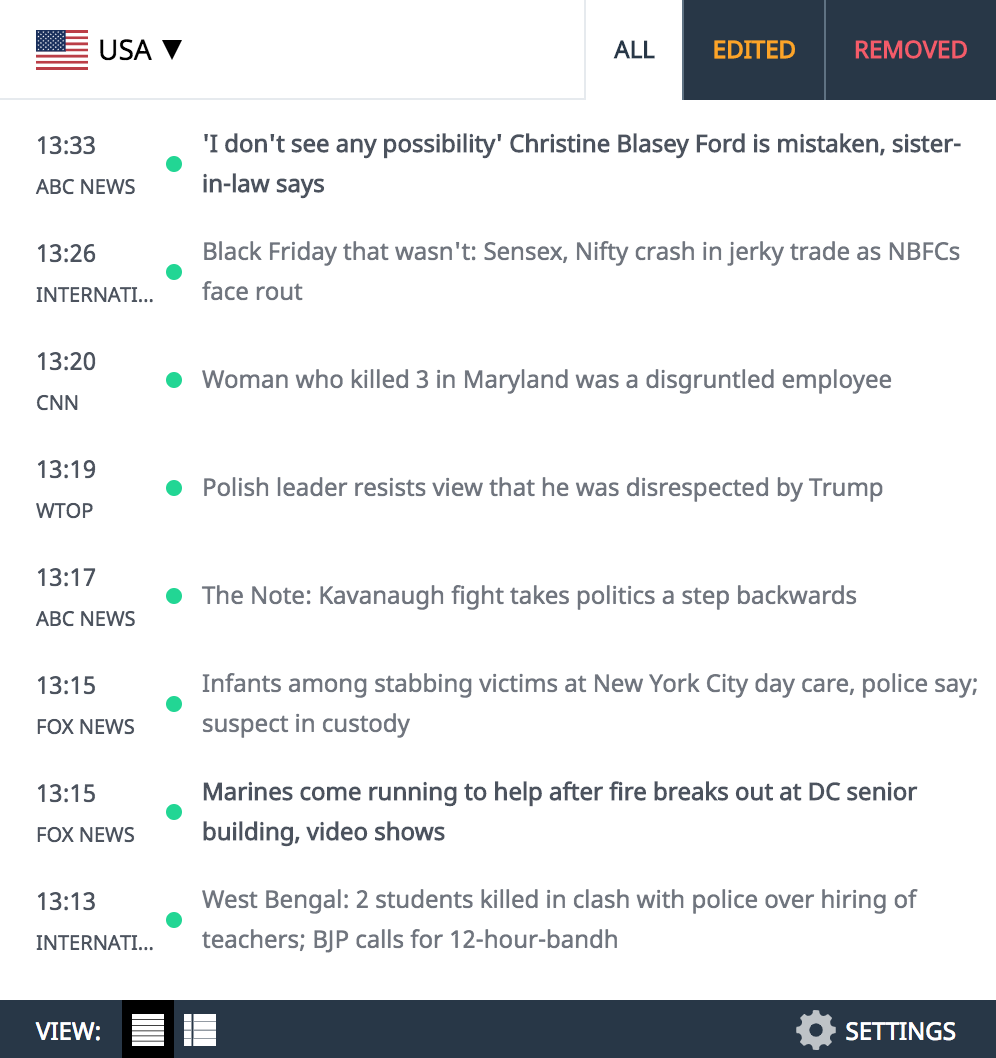
Interesting Creature… Cichlid
Interesting Creatures in Guyana, News
Kaieteur News – Cichlids /ˈsɪklɪdz/ are fish from the family Cichlidae in the order Cichliformes.

The discus, is a genus of cichlids native to the Amazon River basin in South America
Cichlids were traditionally classed in a suborder, the Labroidei, along with the wrasses (Labridae), in the order Perciformes, but molecular studies have contradicted this grouping. The closest living relative of cichlids is probably the convict blenny, and both families are classified in the 5th edition of Fishes of the World as the two families in the Cichliformes, part of the subseries Ovalentaria. This family is both large and diverse. At least 1,650 species have been scientifically described, making it one of the largest vertebrate families. New species are discovered annually, and many species remain undescribed. The actual number of species is therefore unknown, with estimates varying between 2,000 and 3,000.
Many cichlids, particularly tilapia, are important food fishes, while others, such as the Cichla species, are valued game fish. The family also includes many popular freshwater aquarium fish kept by hobbyists, including the angelfish, oscars, and discus. Cichlids have the largest number of endangered species among vertebrate families, most in the haplochromine group. They are particularly well known for having evolved rapidly into many closely related but morphologically diverse species within large lakes. Many cichlids introduced into waters outside of their natural range have become nuisances.
All cichlids practice some form of parental care for their eggs and fry, usually in the form of guarding the eggs and fry or mouthbrooding.
Anatomy and appearance
Cichlids span a wide range of body sizes, from species as small as 2.5 cm (1 in) in length (e.g., female Neolamprologus multifasciatus) to much larger species approaching 1 m (3 ft) in length (Boulengerochromis and Cichla). As a group, cichlids exhibit a similar diversity of body shapes, ranging from strongly laterally compressed species (such as Altolamprologus, Pterophyllum, and Symphysodon) to species that are cylindrical and highly elongated (such as Julidochromis, Teleogramma, Teleocichla, Crenicichla, and Gobiocichla). Generally, however, cichlids tend to be of medium size, ovate in shape, and slightly laterally compressed, and generally similar to the North American sunfishes in morphology, behaviour, and ecology.
Cichlids share a single key trait – the fusion of the lower pharyngeal bones into a single tooth-bearing structure. A complex set of muscles allows the upper and lower pharyngeal bones to be used as a second set of jaws for processing food, allowing a division of labour between the “true jaws” (mandibles) and the “pharyngeal jaws”. Cichlids are efficient and often highly specialised feeders that capture and process a very wide variety of food items. This is assumed to be one reason why they are so diverse.
Feeding
Within the cichlid family, carnivores, herbivores, omnivores, planktivores, and detritivores are known, meaning the Cichlidae encompass essentially the full range of food consumption possible in the animal kingdom. Various species have morphological adaptations for specific food sources, but most cichlids consume a wider variety of foods based on availability. Carnivorous cichlids can be further divided into piscivorous and molluscivorous, since the morphology and hunting behaviour differ greatly between the two categories. Piscivorous cichlids eat other fish, fry, larvae, and eggs. Some species eat the offspring of mouthbrooders by head-ramming, wherein the hunter shoves its head into the mouth of a female to expel her young and eat them. Molluscivorous cichlids have several hunting strategies amongst the varieties within the group. Lake Malawi cichlids consume substrate and filter it out through their gill rakers to eat the mollusks that were in the substrate. Gill rakers are finger-like structures that line the gills of some fish to catch any food that might escape through their gills.
Many cichlids are primarily herbivores, feeding on algae (e.g. Petrochromis) and plants (e.g. Etroplus suratensis). Small animals, particularly invertebrates, are only a minor part of their diets.
Other cichlids are detritivores and eat organic material, called Aufwuchs (offal); among these species are the tilapiines of the genera Oreochromis, Sarotherodon, and Tilapia.
Other cichlids are predatory and eat little or no plant matter. These include generalists that catch a variety of small animals, including other fishes and insect larvae ((e.g. Pterophyllum), as well as variety of specialists. (Source: Wikipedia)